Jan 29, 2026

In many industrial piping systems, valve failure is rarely caused by extreme pressure or temperature. More often, it is the high operating frequency that shortens valve service life. In steam lines, water circulation systems, automated production equipment, or testing rigs, valves may cycle hundreds or even thousands of times per day. Under such conditions, frequent opening and closing become the primary source of mechanical wear.
This is where the globe valve shows a clear structural advantage compared with rotary valves such as ball valves or butterfly valves.
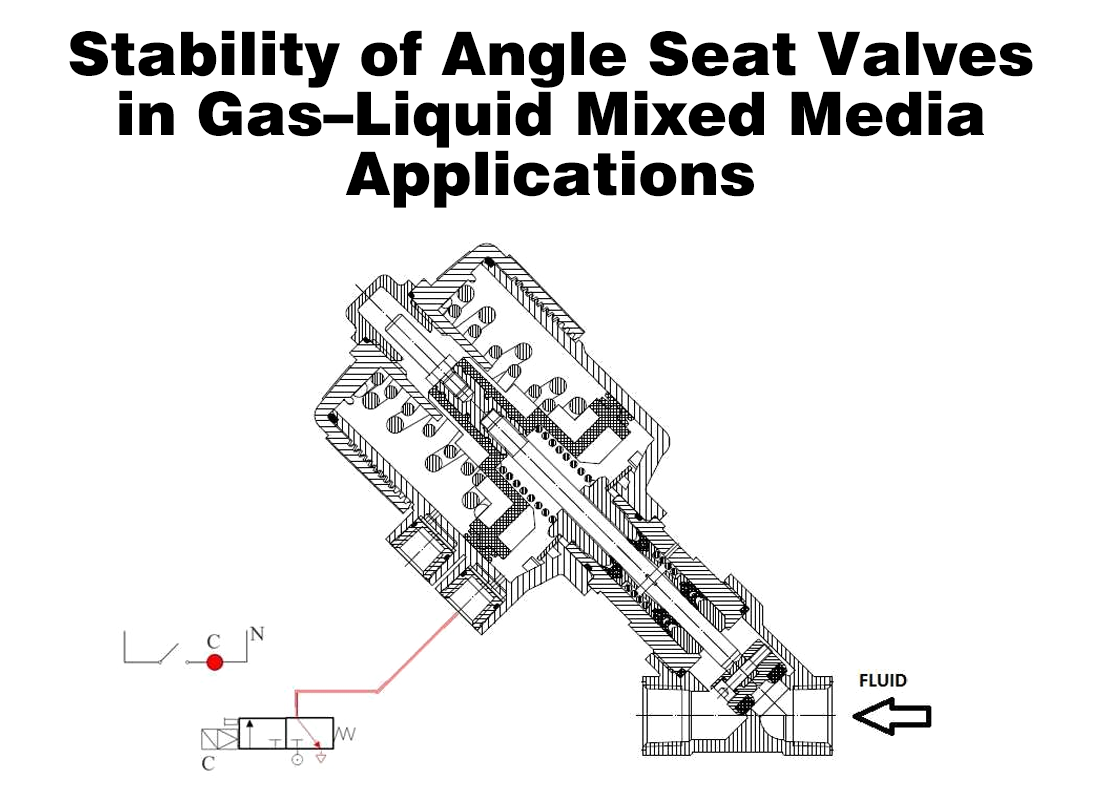
Every valve closure involves direct contact between the valve disc and the valve seat. When this contact occurs repeatedly, the way force is applied becomes critical. Poor contact geometry leads to localized stress, accelerated wear, and eventually internal leakage.
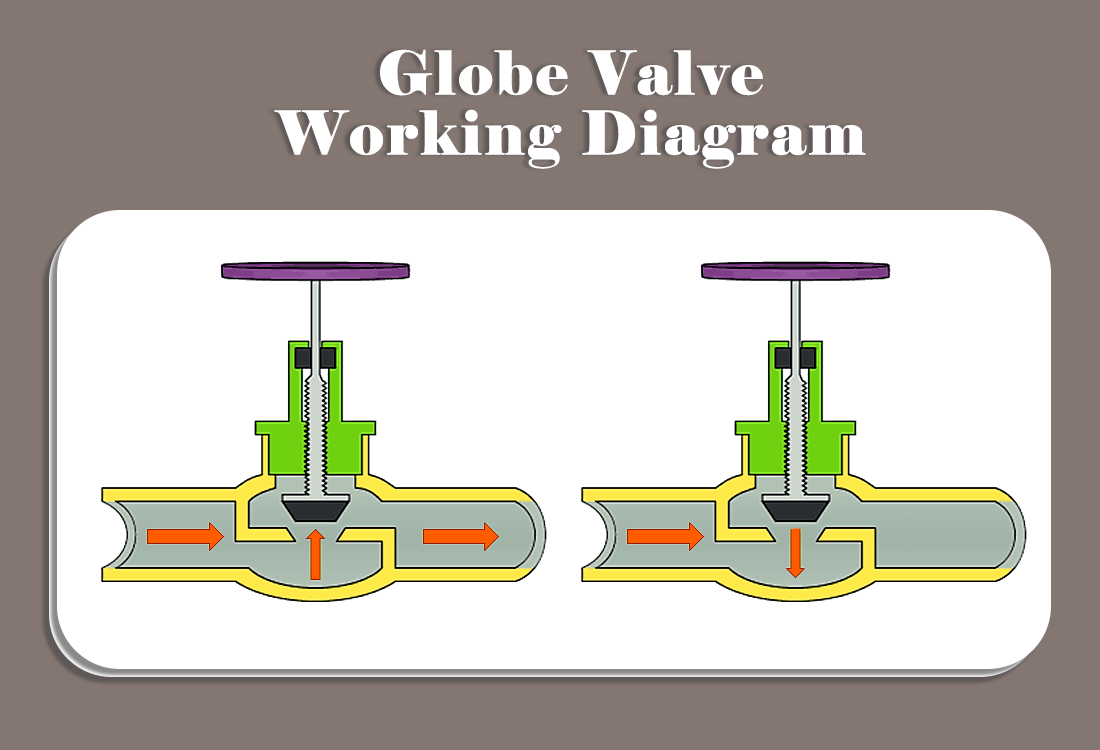
Rotary valves typically close by sliding or sweeping the sealing surface across the seat. Under high pressure or fast actuation, this sliding contact concentrates stress on small areas, creating wear tracks that degrade sealing performance over time.
A globe valve behaves differently. The disc moves axially along the stem, pressing directly onto the seat. This vertical contact avoids lateral scraping and significantly reduces uneven wear.
The defining feature of a globe valve is its linear lift mechanism. During both opening and closing, the disc maintains a consistent motion path and force direction. There is no rotation-induced side load on the sealing surfaces.
This design brings several long-term benefits:
◆ Even stress distribution on the valve seat
◆ Reduced seal fatigue under high-cycle operation
◆ Predictable flow control with minimal hydraulic shock
In systems where valves cycle frequently, reliability and consistency matter more than achieving the lowest possible pressure drop.
Ball valves and butterfly valves excel in quick shut-off applications, but they are not inherently designed for continuous cycling. As switching frequency increases, rotary valves often face:
◆ Concentrated seat wear
◆ Strong fluid impact at closing
◆ Increased vibration and operating noise
By contrast, the globe valve’s linear motion produces a smoother closing profile. The gradual engagement between disc and seat helps absorb fluid momentum, making it better suited for frequent operation scenarios.
When dealing with frequent opening and closing, selecting the right valve structure is more critical than choosing premium materials. An unsuitable design cannot be compensated by expensive sealing compounds.
Once the globe valve structure is selected, materials can then be optimized:
◆ Stainless steel globe valves for corrosive media
◆ Metal-seated globe valves for high-temperature service
◆ PTFE seals for precise low-pressure flow control
This sequence—structure first, materials second—is essential for long-term reliability.
Another often-overlooked advantage of globe valves is their ability to reduce operational noise. Because flow changes occur gradually as the disc moves linearly, pressure fluctuations are smoother. This helps minimize water hammer, vibration, and stress on downstream equipment.
For automated systems that cycle continuously, quieter operation is not just a comfort issue—it directly affects system stability and component lifespan.
Frequent cycling itself is not the problem. The real issue is forcing a valve design to operate outside its mechanical comfort zone. Globe valves are not universal solutions, but for high-cycle conditions, their linear lift geometry, uniform sealing contact, and predictable behavior make them a more dependable choice.
For engineers focused on long-term performance rather than short-term flow efficiency, the globe valve offers durability that rotary valves struggle to match.
(FK9025)
 How Air Cylinders Are Actually Used in Industrial Automation Design
How Air Cylinders Are Actually Used in Industrial Automation Design
 Why Globe Valve Performs Better in Frequent Opening and Closing Applications
Why Globe Valve Performs Better in Frequent Opening and Closing Applications
 Rubber hose vs Polyurethane tubing vs Nylon tubing: Choosing the Right Pneumatic Hose Material
Rubber hose vs Polyurethane tubing vs Nylon tubing: Choosing the Right Pneumatic Hose Material
 How Does Mesh Affect the Performance of Pneumatic Silencers?
How Does Mesh Affect the Performance of Pneumatic Silencers?
 Hydraulic Quick Couplers: Maintenance Details Most People Overlook
Hydraulic Quick Couplers: Maintenance Details Most People Overlook
You May Interest In


Dec 12, 2025 Blog
What Is a Globe Control Valve?

Dec 11, 2025 Blog
Two ways for a globe valve to be bidirectional
Dec 10, 2025 Blog
How Does a Manual Globe Control Valve Work?

Dec 08, 2025 Blog
Can a Globe Valve Be Used to Control Steam Pressure
Dec 08, 2025 Blog
How Does a Globe Valve Work
Dec 04, 2025 Blog
How to Identify Gate Valve and Globe Valve

Dec 09, 2025 Blog
Working Principle of Check Valves

Dec 06, 2025 Blog
How to check pneumatic solenoid valve?

Dec 04, 2025 Blog
How does a single solenoid valve work?
Dec 03, 2025 Blog
What is double acting solenoid valve?
Dec 02, 2025 Blog
How to clean a pneumatic solenoid valve?
Dec 01, 2025 Blog
How to Wire and Install a Pneumatic Solenoid Valve?
Nov 30, 2025 Blog
How to select pneumatic solenoid valve?Links: www.fescolo.com(Pneumatic)
FOKCA ©1998-2025 All Rights Reserved Sitemap