Dec 03, 2025
A double-acting solenoid valve is a type of pneumatic solenoid valve used to control double-acting cylinders. In a double-acting cylinder, air pressure is used to drive the cylinder in both directions—extension and retraction. Unlike single-acting cylinders, which rely on a spring for return, the movement of a double-acting cylinder in both directions requires control by an air supply.
A double-acting solenoid valve is a type of solenoid valve specifically designed for complex system structures.The key components of a double acting solenoid valve are different from those of a single acting valve,the following are its main structural components:
Two coils: two independent electromagnetic coils located at both ends of the valve.
Valve core: a component that slides in a precision inner hole and connects or blocks the flow path through its shoulder and groove.
Valve body: includes an inner hole for the valve core and an external interface.
Sealing element: prevents leakage between the valve core and valve body.
The most crucial thing is that it does not have a spring like the single solenoid valve. The switching and maintenance of the valve core rely entirely on electromagnetic force and fluid pressure.
A typical five port two position (5/2) double acting solenoid valve is commonly used to control double acting cylinders. It has five interfaces: an intake port (P), two exhaust ports (R, S), and two working ports (A, B).
Action: Send a brief electrical pulse to coil A.
Valve core movement: The magnetic force generated by coil A pushes the valve core to move to the right.
Flow path:
The gas source flows from port P to port A.
Connect port B to exhaust port S.
This usually drives the cylinder to extend.
Maintain position: After the valve core moves to the right position, the fluid pressure acting on both ends will firmly hold it in this position, even if the pulse signal of coil A has disappeared. The valve "remembers" this state.
Action: Send a brief electrical pulse to coil B.
Valve core movement: The magnetic force generated by coil B pulls the valve core to move to the left.
Flow path:
The gas source flows from port P to port B.
Connect port A to exhaust port R.
This usually drives the cylinder to retract.
Maintain position: Similarly, fluid pressure will firmly hold the spool in this new left position. The valve "remembers" this new state.
When there is a power outage, this is the most important difference between double acting valves and single acting valves:
When both coils are powered off, the valve will not operate. It will remain in its last triggered position.
This is a 'hold' or 'memory' function. If the power supply is interrupted, the cylinder controlled by this valve will remain extended or retracted.
| Feature | Single-Acting Solenoid Valve | Double-Acting Solenoid Valve |
|---|---|---|
| Number of Coils | One | Two |
| Return Mechanism | Spring | Fluid Pressure |
| Default State | Yes (Normally Open or Normally Closed) | No. It has two stable working positions. |
| State after Power Loss | Returns to the spring-default position. | Remains in the last active position. |
| Power Consumption | Power required only to actuate against the spring (in one direction). | Requires only a brief pulse signal to change state; does not need continuous power. |
| Common Symbol | 3/2 (3-port, 2-position) | 5/2 (5-port, 2-position) or 4/2 (4-port, 2-position) |
| Controlled Actuator Type | Single-Acting Cylinder (with a spring) | Double-Acting Cylinder (without a spring) |
Double acting solenoid valves are crucial for controlling double acting cylinders, as both the extension and retraction of the cylinder require power.
Industrial automation: robot arms, fixtures, stamping machines.
Material handling: conveyor belt baffle, pusher, elevator.
Automotive manufacturing: used for welding and assembly lines.
Packaging machinery: used for complex power driven actions.
Controlling a double-acting cylinder to extend and retract a robotic arm.
the upward and downward movement of the hydraulic press slide.
| Item | Double-Acting Pneumatic Solenoid Valve | Double-Acting Hydraulic Solenoid Valve |
|---|---|---|
| Working Medium | Compressed air | Hydraulic oil |
| Typical Working Pressure | 0.3–0.8 MPa (low pressure) | 10–35 MPa (high pressure), or higher |
| Actuator Driven | Double-acting pneumatic cylinder | Double-acting hydraulic cylinder |
| Main Applications | Light-load, high-speed motion | Heavy-load, high-force, precise control |
| Valve Body Materials | Aluminum alloy, plastics, lightweight materials | Steel, cast iron, reinforced metal structures |
| Response Speed | Fast, suitable for high-frequency actuation | Slower, but more stable and powerful |
| Control Precision | Medium (air is compressible) | High (liquids are essentially incompressible) |
| Common Valve Types | 5/2, 4/2 double-solenoid valves | 4/3, 4/2 double-solenoid directional control valves |
| Load Level | Light to medium loads | Medium to heavy loads |
| Leakage Impact | Air leakage acceptable | Oil leakage serious (contamination + efficiency loss) |
| Maintenance Difficulty | Low, clean system | Higher, requires fluid cleanliness and sealing maintenance |
Other websites related to manufacturing:
Answer: Leaks are usually caused by damaged or worn seals, dirt or debris inside the valve, improper installation, or excessive pressure. Regular maintenance and proper installation can prevent leaks.
Answer: A normally open 2-way solenoid valve stays open when unpowered and closes when powered. It is suitable for controlling water, oil, or air flow in simple on/off applications.
Answer: Material choice depends on the fluid type, pressure, temperature, and corrosion resistance requirements:
Plastic: lightweight, chemical resistance, low pressure
Brass: durable, moderate pressure, common in water/oil/air
Stainless steel: high corrosion resistance, suitable for harsh or high-temperature conditions
Answer: Reversing inlet and outlet may cause the valve to malfunction, reduce flow efficiency, or damage seals. Always follow the manufacturer’s flow direction markings.
Answer: You can test by applying the correct voltage and observing the valve action (opening/closing). Additionally, measure coil resistance with a multimeter to check for continuity or shorts.
(9016)
 Impact of Trapped Media in the Valve Cavity on Restart Performance of Pneumatic Ball Valves
Impact of Trapped Media in the Valve Cavity on Restart Performance of Pneumatic Ball Valves
 Wear Path Analysis of Pneumatic Ball Valve Under Frequent Cycling Conditions
Wear Path Analysis of Pneumatic Ball Valve Under Frequent Cycling Conditions
 Mini Push In Fittings: Aging Problems of Plastic Bodies in Humid Environments
Mini Push In Fittings: Aging Problems of Plastic Bodies in Humid Environments
 Mini Type Pneumatic Push In Fittings: Flow Difference Between Straight and Elbow Designs
Mini Type Pneumatic Push In Fittings: Flow Difference Between Straight and Elbow Designs
 Influence of Exhaust Throttling of 3-Way Solenoid Valve on Actuator Return Speed
Influence of Exhaust Throttling of 3-Way Solenoid Valve on Actuator Return Speed
You May Interest In



Dec 02, 2025 Blog
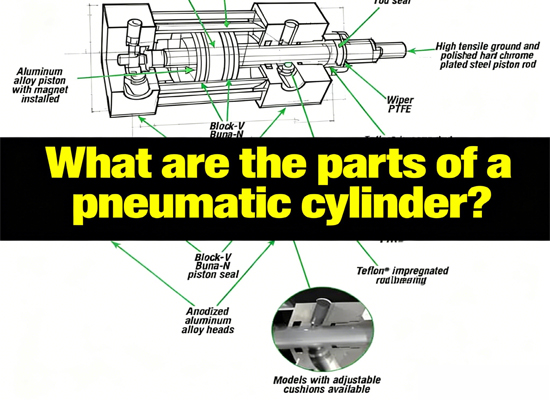
What are the parts of a pneumatic cylinder?












Apr 18, 2025 Blog
What is an Angle Seat Valve?Links: www.fescolo.com(Pneumatic)
FOKCA ©1998-2025 All Rights Reserved Sitemap