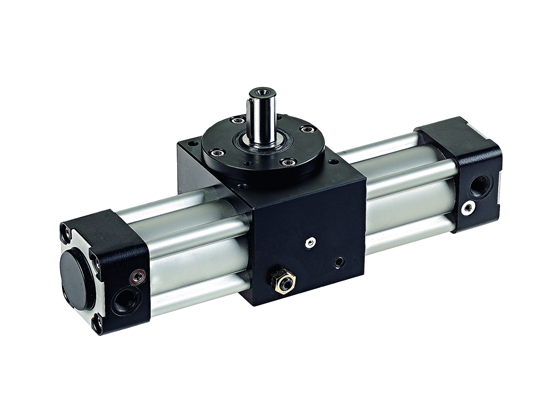
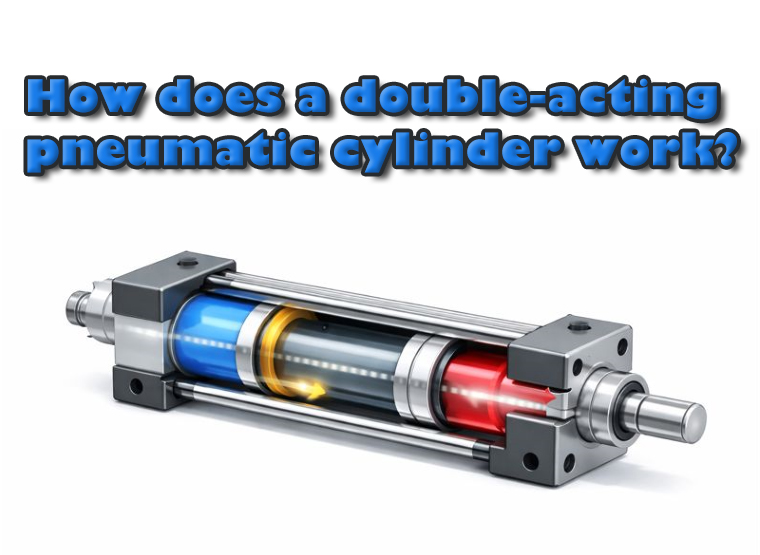
What Is A Double Acting Cylinder?
Double-acting and single-acting are the two main actuation types of pneumatic cylinders.The difference lies in how the driving medium pushes the piston to move.
A double-acting cylinder has both pneumatic and hydraulic types,and a double-acting pneumatic cylinder is a kind of actuator that allows the piston to move back and forth in both directions through the action of a fluid medium. Compressed air alternately enters both sides of the piston, enabling bidirectional motion — extension and retraction — under air pressure.In contrast, a single-acting cylinder uses compressed air from only one inlet port to drive the piston in a single direction, while the return stroke relies on a spring or external force rather than air pressure.
Function of a Double Acting Cylinder
◆ Bidirectional Motion:
The most distinctive feature of a Double Acting Cylinder is that its piston can move the load in both directions.
◆ Higher Output Force:
Since a Double Acting Cylinder has no internal spring structure, both the extension and retraction of the piston rod are driven by compressed air. As a result, this type of cylinder can handle heavier loads.
◆ Versatile Expandability:
Various functional components and accessories can be mounted on the outer surface of the cylinder barrel, including fixtures for mounting, stroke sensors, cushioning adjusters, and position feedback devices.
◆ More Precise Control of Speed and Stroke:
Because both ends of the piston are powered by compressed air, the movement of the piston rod can be controlled precisely in both directions.
Applications of Double Acting Cylinders
◆ Automated Production Lines:
Pneumatic double acting cylinders can be rapidly driven by air pressure from both directions, enabling quick pushing and pulling actions.
◆ Packaging and Printing Machinery:
In packaging and printing processes that require box pushing, sealing, or roller adjustment, the bidirectional motion of the cylinder allows smooth extension and retraction, ensuring stable operation.
◆ Machine Tools and Pressing Fixtures:
In machine tool fixtures and press-fitting equipment, double acting cylinders can provide consistent clamping and releasing force in both directions.
Hydraulic double acting cylinders are suitable for heavy-duty pressing and high-precision tooling control.
◆ Conveying and Sorting Systems:
In conveyor lines and sorting machines, pneumatic double acting cylinders use their bidirectional drive to achieve reciprocating positioning and switching of materials.
◆ Hydraulic Presses and Injection Molding Machines:
Hydraulic double acting cylinders, driven by high-pressure oil, enable powerful and stable bidirectional piston motion, delivering the strong force required for heavy industrial machinery.
How Does A Double Acting Pneumatic Cylinder Work?
Basic Structure of a Double-Acting Cylinder
A double-acting cylinder typically includes:
Cylinder tube: A cylindrical chamber that houses the piston.
Piston: Moves back and forth inside the cylinder.
Piston rod: Connects to the piston and transmits force to the load.
Two ports (Port A and Port B): Connected to compressed air lines, used to drive the piston in different directions.
Seals: Prevent air leakage.
The key feature of a double-acting cylinder is that compressed air can drive the piston both forward and backward. Unlike a single-acting cylinder, which usually relies on a spring or external force for return.
Working Principle
A actuator double action cylinder achieves reciprocating motion by controlling which chamber the air enters.
Piston Chamber Division
Front chamber: The side of the cylinder where the piston rod exits.
Rear chamber (Rod Side): The opposite side of the piston rod, usually slightly smaller in volume than the front chamber.
Operating Process
Forward Stroke
Compressed air enters the front chamber through Port A, pushing the piston toward the rod side.
At the same time, air in the rear chamber is exhausted through Port B.
The piston rod extends, performing work on the load.
Return Stroke
Compressed air enters the rear chamber through Port B, pushing the piston backward.
Air in the front chamber is exhausted through Port A.
The piston rod retracts.
By controlling the air supply and using a directional control valve, the piston can perform precise reciprocating motions.
How Does A Double Acting Hydraulic Cylinder Work?
Basic Structure
The two main moving components of a hydraulic cylinder are the piston and piston rod. The two ports at the front and rear ends are used for the inlet and outlet of the working fluid.
Forward Stroke (Piston Extension)
The hydraulic pump delivers fluid into port A, pushing the piston forward. The fluid in port B is discharged back to the reservoir.
Return Stroke (Piston Retraction)
Fluid enters port B, pushing the piston backward. The fluid in port A is discharged back to the reservoir.
Features:
Bidirectional control: Both extension and retraction are controlled by hydraulic pressure.
High and stable thrust: Provides greater and smoother force than a double-acting pneumatic cylinder, suitable for heavy loads and precise movements.
Flexible stroke length: Stroke can be adjusted, and motion speed is controllable.
Advantages of Double-Acting Cylinder Compared Single-Acting
Simpler structure;
lower air consumption
Disadvantegs
output force is limited by the spring's counterforce and therefore smaller;
return speed of the piston rod cannot be adjusted;
shorter service life and requires frequent maintenance.
Double acting advantages
High-frequency opening and closing with bidirectional control;
greater output force with balanced extension and retraction;
bidirectional speed adjustable via airflow;
longer service life with less frequent maintenance;
lighter and more compact in size and weight.
Disadvantegs
slightly more complex structure;
higher air consumption;
cannot automatically return when air supply is cut off, external measures required.
| Feature | Single-Acting Cylinder | Double-Acting Cylinder |
|---|
| Motion Direction | One-way (typically air pushes, return by spring or external force) | Two-way (hydraulic/air pushes in both directions) |
| Number of Ports | 1 port | 2 ports |
| Return Method | Spring, gravity, or external force | Pressure-controlled (air or hydraulic) |
| Structural Complexity | Simple, fewer pipelines | More complex, more pipelines |
| Cost | Lower | Higher |
| Control Valve Type | 3/2 valve is sufficient | 4/2 or 5/2 valve |
| Motion Accuracy | Return depends on spring, moderate accuracy | Precise control in both forward and return strokes |
| Applicable Stroke | Short strokes are more common | Suitable for short or long strokes |
| Operating Frequency | Low to medium frequency | Medium to high frequency or high-speed operation |
Conclusion
If your application only requires force in one direction and no force in the return stroke, you can choose a single-acting cylinder.
For low-frequency and simple motions, a single-acting actuator is also suitable.
If your system must automatically return to its initial position when the air supply is interrupted, then a single-acting type is required.
If your application requires force in both directions, you should choose a double-acting actuator.
If your system needs stable and adjustable speeds, a double-acting actuator is also appropriate.
For tasks that demand high thrust or heavy loads, as well as applications with high-frequency motion or long service life requirements, you can choose a double-acting actuator.