Nov 12, 2025

A single acting cylinder is a pneumatic actuator that delivers force in one direction only, while the return movement is achieved mechanically rather than by air pressure. In industrial automation, it is typically selected for its defined default position, predictable behavior during air loss, and simplified system logic, rather than for basic motion requirements.
On paper, a single acting cylinder may seem like a simplified alternative to a double acting design. In practice, the real differences only become visible once the cylinder is installed and operating under real production conditions.
Because compressed air is applied to only one side of the piston, system behavior during pressure loss, startup, and emergency stops follows a different logic. These differences directly affect force availability, safety response, maintenance strategy, and long-term operating stability.
For experienced engineers, this is where the choice between single acting and double acting cylinders actually matters.
The most common misjudgment when applying a single acting cylinder is assuming that theoretical force equals usable force.
In spring return designs, part of the generated force is continuously consumed by the return mechanism. The spring preload and compression curve reduce effective thrust throughout the working stroke. Increasing air pressure alone rarely compensates for this loss and can introduce instability or accelerated wear.
In applications such as clamping, forming, or high-friction positioning, engineers often achieve better results by selecting a larger bore or specifying a custom single acting cylinder with optimized spring characteristics, rather than pushing the system closer to its pressure limits.
In many automation systems, a single acting cylinder is not simply a motion component—it is part of the safety strategy.
When air supply is interrupted, the cylinder automatically returns to a mechanically defined position without relying on PLC logic, sensors, or electrical power. This passive response is particularly valuable in:
· Tool withdrawal during emergency stops
· Automatic workpiece release in fixture systems
· Mechanical reset after air or power loss
From a system validation perspective, this behavior reduces dependency on control-layer redundancy and simplifies risk assessment.
In high-frequency production environments, the dominant failure mode of a single acting pneumatic cylinder is often misunderstood.
While seal wear is a common concern in double acting designs, spring fatigue becomes the limiting factor in single acting cylinders. Short strokes combined with high cycle rates place continuous mechanical stress on the return spring, gradually affecting response speed and return reliability.
To address this, experienced engineers may:
· Reduce spring rates while increasing bore size
· Minimize stroke length wherever possible
· Specify reinforced or specially treated springs
These design decisions significantly influence service life but are rarely visible in standard catalog data.
From a purely functional standpoint, a double acting cylinder offers more control flexibility. However, in many machines, that flexibility adds complexity without real benefit.
When force is required in only one direction and the return stroke serves primarily as a reset, a single acting cylinder eliminates the need for return-side flow control, additional valve ports, and complex fault-handling logic.
The result is a system that is easier to commission, easier to troubleshoot, and more predictable under abnormal conditions.
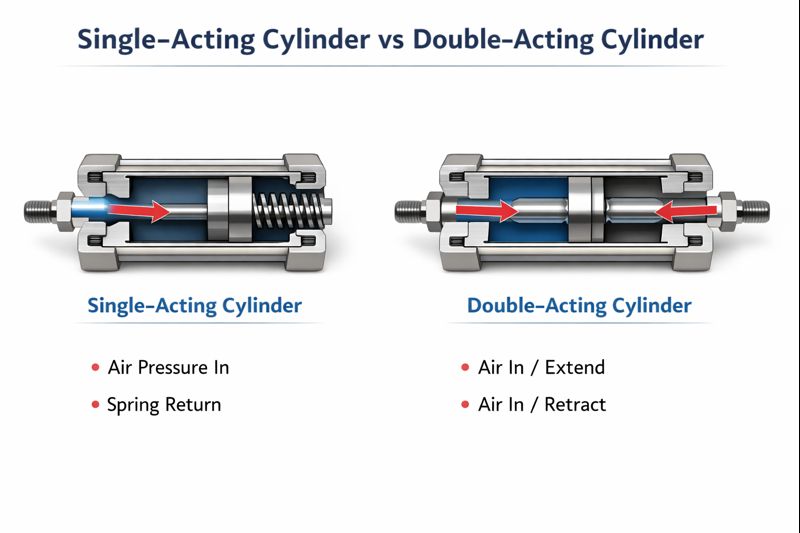
At this stage, the differences discussed above can be summarized clearly.
Aspect | ||
Air pressure usage | One direction only | Both directions |
Return movement | Spring or external force | Air pressure |
Position on air loss | Mechanically defined | Control-dependent |
Effective output force | Reduced by spring force | Full theoretical force |
Valve requirement | 3/2-way valve | 5/2 or 4/2-way valve |
Control complexity | Lower | Higher |
Typical application focus | Safety, reset logic, efficiency | Continuous bidirectional motion |
Return behavior in a single acting cylinder is closely tied to installation conditions. Gravity, friction, and side loads all influence how reliably the piston returns to its default position.
In gravity-assisted designs, improper orientation can lead to delayed or incomplete retraction. Even spring return cylinders can behave inconsistently if mounting alignment increases friction beyond expected limits.
For non-vertical or space-constrained installations, custom cylinder structures or guided designs are often required to ensure long-term stability.
Standard single acting cylinders perform well in short-stroke, moderate-load applications. Limitations become evident when systems demand:
· Long strokes with controlled return speed
· High ambient temperatures affecting spring behavior
· Continuous operation with minimal tolerance for downtime
In such cases, OEMs often move toward custom single acting cylinder solutions, adjusting spring geometry, materials, or integrating external return forces to maintain reliable performance.
As automation systems grow more complex, experienced engineers increasingly favor components that reduce dependence on control logic rather than expand it.
A single acting cylinder embeds mechanical logic directly into the system. It behaves correctly not because it is actively controlled, but because it is designed to respond predictably—even when air, power, or control signals are lost.
That characteristic keeps it relevant not as a basic actuator, but as a deliberate engineering choice in modern industrial equipment.
(FK9027)
 Mini Type Pneumatic Push In Fittings: Flow Difference Between Straight and Elbow Designs
Mini Type Pneumatic Push In Fittings: Flow Difference Between Straight and Elbow Designs
 Influence of Exhaust Throttling of 3-Way Solenoid Valve on Actuator Return Speed
Influence of Exhaust Throttling of 3-Way Solenoid Valve on Actuator Return Speed
 Influence of Coil Overheating on Continuous Duty of 2-Way Solenoid Valve
Influence of Coil Overheating on Continuous Duty of 2-Way Solenoid Valve
 PVC Flexible Tubing vs PU Tubing: Cost Difference Analysis in Equipment Internal Routing
PVC Flexible Tubing vs PU Tubing: Cost Difference Analysis in Equipment Internal Routing
 The principle and characteristics of vacuum generators
The principle and characteristics of vacuum generators
You May Interest In
Links: www.fescolo.com(Pneumatic)
FOKCA ©1998-2025 All Rights Reserved Sitemap