Nov 13, 2025

Valve seat angles are critical to the performance of valves in a wide range of systems, from industrial pneumatic applications to automotive engines. A precise valve seat angle is essential for achieving a proper seal, efficient fluid or gas flow, and long-term reliability of the valve. In this guide, we’ll delve into the process of checking valve seat angles, the tools required, and the potential consequences of an improper angle.
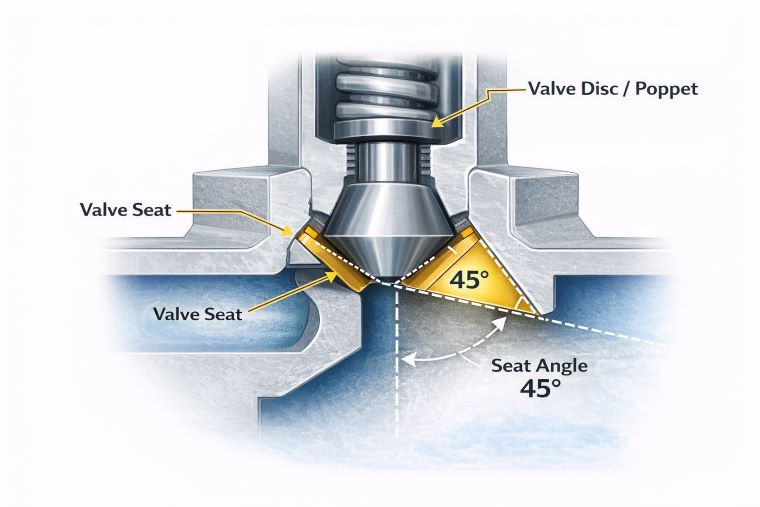
The valve seat is the surface within the valve body where the valve disc or ball rests when the valve is closed. The angle of the valve seat refers to its inclination in relation to the valve body and plays a critical role in the valve’s ability to form a tight seal. An incorrect valve seat angle can cause a range of issues, from poor sealing to reduced flow efficiency and increased wear on both the valve seat and disc.
In applications such as pneumatic systems, where air or fluid control is crucial, an improperly angled seat can lead to leaks, reduced system performance, and higher energy consumption. It is essential to measure and adjust the seat angle to match the manufacturer’s specifications to ensure the valve functions as intended.
To accurately measure and adjust a valve seat angle, you’ll need several specific tools:
Protractor or Angle Gauge
A protractor (either mechanical or digital) is necessary to measure the exact angle of the valve seat. Precision is key, as small deviations can impact valve performance.
Valve Seat Cutter
If adjustments are required, a valve seat cutter will be used to modify the angle. This tool comes in both manual and powered versions, depending on the valve size and design.
Dial Gauge
This tool checks the concentricity and depth of the valve seat, ensuring that the surface is uniformly aligned and properly angled.
Micrometer
A micrometer measures the seat’s diameter and thickness, ensuring it is the correct size for the valve disc.
1. Remove the Valve from the System
Before inspecting the valve seat, remove the valve from the system. This allows you to work on the valve independently and check the seat for any visible wear or damage.
2. Inspect the Valve Seat
After removal, examine the valve seat for signs of wear, corrosion, or other damage. A well-maintained valve seat should have a smooth, even surface. Any visible damage could affect the valve's sealing ability and may require re-machining or replacement.
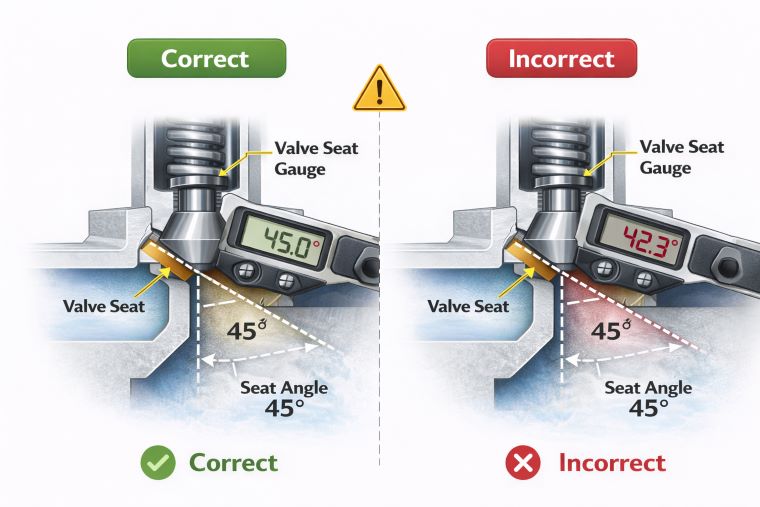
3. Measure the Valve Seat Angle
Using your angle gauge, measure the angle of the valve seat. This angle should match the manufacturer’s specifications for optimal performance. Common valve seat angles typically range from 30° to 70°, depending on the application and system type. For example, engine valves often use a 45° to 60° angle, while industrial valves may use a wider range, depending on the specific fluid or gas they control.
4. Check for Consistency Across the Seat
Use the dial gauge to check the uniformity of the seat’s angle. It is crucial to ensure that the seat maintains a consistent angle across the entire surface. Even slight variations can compromise the valve’s performance and cause uneven wear.
5. Adjust the Valve Seat Angle (If Necessary)
If the valve seat angle is incorrect or inconsistent, use the valve seat cutter to adjust it. Make small adjustments and check the angle frequently to ensure accuracy. Avoid over-cutting, as this could damage the valve seat and affect the valve’s ability to seal properly.
Over-Cutting the Seat
One common mistake when adjusting valve seat angles is over-cutting, which can change the size and shape of the seat, leading to poor sealing. To avoid this, make gradual adjustments and measure frequently.
Inconsistent Angles Across the Seat
Variations in the valve seat angle can cause uneven wear and leakage. Ensure that the cutting tool is aligned correctly and make small, uniform adjustments to the entire seat.
Contamination on the Valve Seat
Dust or debris can affect the measurement process and cause inaccurate readings. Always clean the valve seat thoroughly before performing any measurements or adjustments.
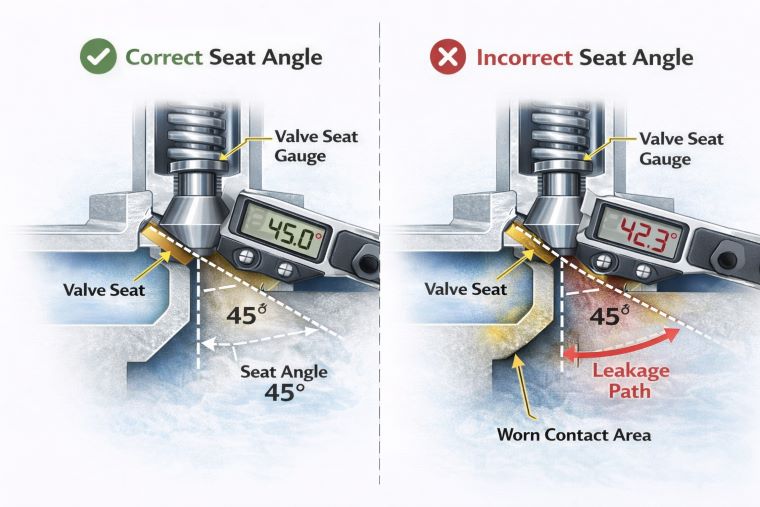
An improperly angled valve seat can result in several issues that affect both performance and longevity:
Improper Seal
A valve seat with the wrong angle may not seal properly, allowing air or fluid to leak past the valve. This can lead to reduced pressure, energy inefficiency, and operational disruptions.
Reduced Flow Efficiency
If the valve seat angle is incorrect, it can disrupt the flow of air or fluid, leading to turbulence, reduced flow rates, and energy loss. This is particularly critical in pneumatic systems, where smooth air flow is necessary for optimal performance.
Increased Wear
An incorrect angle can cause uneven wear on both the valve seat and valve disc, leading to the need for more frequent maintenance or replacements.
(FK9027)
 Mini Type Pneumatic Push In Fittings: Flow Difference Between Straight and Elbow Designs
Mini Type Pneumatic Push In Fittings: Flow Difference Between Straight and Elbow Designs
 Influence of Exhaust Throttling of 3-Way Solenoid Valve on Actuator Return Speed
Influence of Exhaust Throttling of 3-Way Solenoid Valve on Actuator Return Speed
 Influence of Coil Overheating on Continuous Duty of 2-Way Solenoid Valve
Influence of Coil Overheating on Continuous Duty of 2-Way Solenoid Valve
 PVC Flexible Tubing vs PU Tubing: Cost Difference Analysis in Equipment Internal Routing
PVC Flexible Tubing vs PU Tubing: Cost Difference Analysis in Equipment Internal Routing
 The principle and characteristics of vacuum generators
The principle and characteristics of vacuum generators
You May Interest In

Apr 18, 2025 Blog
What is an Angle Seat Valve?
Nov 13, 2025 Blog
What are pneumatic angle seat valves used for?Links: www.fescolo.com(Pneumatic)
FOKCA ©1998-2025 All Rights Reserved Sitemap