Feb 10, 2026

In many automation systems, a 2 way solenoid valve is required to stay energized for hours, such as pressure holding in water treatment or standby in industrial automation. Under this condition, heat accumulates inside the coil while ventilation is often limited. Field experience shows that excessive temperature rise reduces magnetic force, leading to unstable actuation of the spool and abnormal flow.
When temperature increases, the resistance of the copper winding rises and the current decreases. For direct acting 2 way solenoid valve, the pull force may not overcome the spring. In pilot operated 2 way solenoid valve, insufficient pilot pressure results in delayed opening. Many normally closed 2 way solenoid valve failures are actually thermal problems rather than mechanical sticking.
Overheating also affects materials. The housing of a sealed 2 way solenoid valve can deform slightly, increasing friction. Elastomer seals harden and lose elasticity, especially in 2 way solenoid valve for steam or hot water applications. This shortens service life dramatically.
| Influence Item | Direct Result | System Symptom |
|---|---|---|
| Coil resistance rise | Current drop | Slow opening |
| Magnetic force reduction | Insufficient pull | Valve cannot stay energized |
| Insulation aging | Short circuit risk | Coil burn |
| Plastic deformation | Spool friction | Unstable flow |
| Seal hardening | Leakage | Pressure loss |
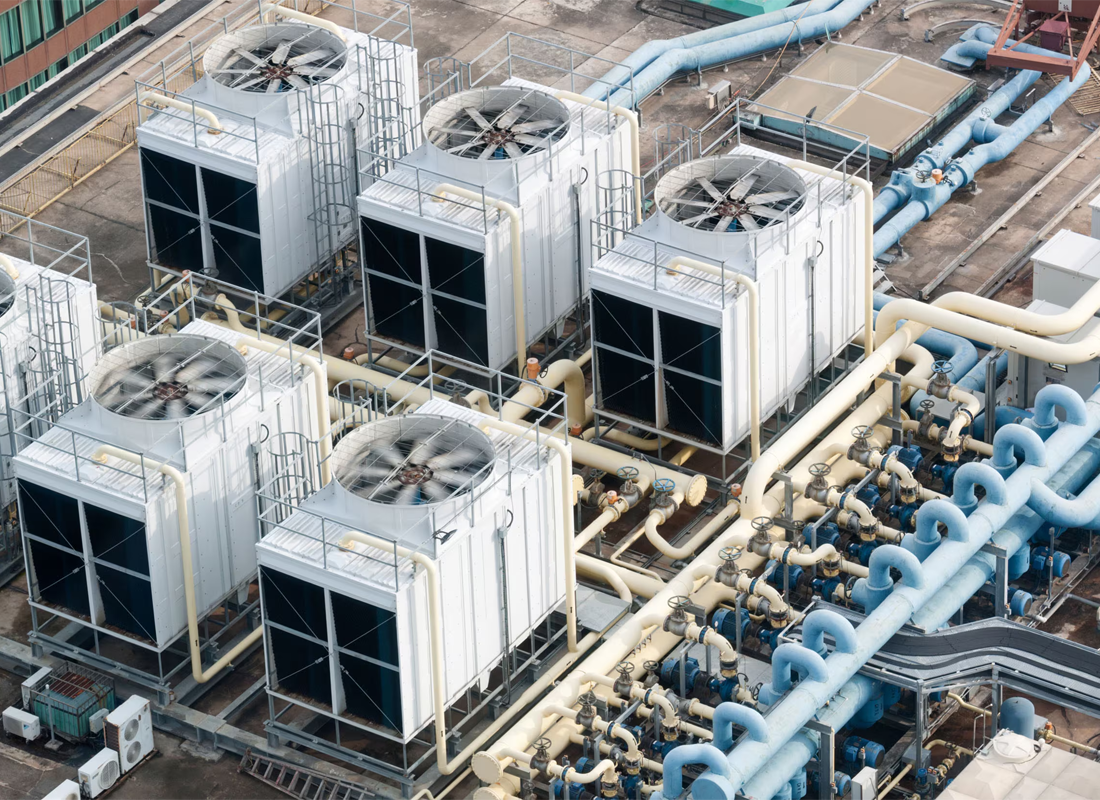

A 2 way pneumatic solenoid valve with frequent air flow gains natural cooling, while valves in 2 way solenoid valve for HVAC or water treatment remain energized without cooling. High pressure 2 way solenoid valve bodies store more heat and require higher insulation class. Ignoring duty cycle in the 2 way solenoid valve sizing chart is a common selection mistake.
Voltage deviation directly changes coil power. The 2 way solenoid valve coil voltage comparison shows DC coils are sensitive to line drop. Mounting on metal brackets helps heat dissipation, while enclosed plastic boxes trap heat and accelerate aging.
◆ Use low power or continuous-duty coils
◆ Design rest intervals in 2 way solenoid valve control system
◆ Follow 2 way solenoid valve maintenance tips to check resistance
◆ Choose proper type for 2 way solenoid valve for chemical process or water systems
When deciding between different types such as 2 way solenoid valve vs 3 way solenoid valve, understanding thermal behavior is as important as flow capacity. Correct design protects reliability and avoids unnecessary replacement.
(FK9025)
 Mini Type Pneumatic Push In Fittings: Flow Difference Between Straight and Elbow Designs
Mini Type Pneumatic Push In Fittings: Flow Difference Between Straight and Elbow Designs
 Influence of Exhaust Throttling of 3-Way Solenoid Valve on Actuator Return Speed
Influence of Exhaust Throttling of 3-Way Solenoid Valve on Actuator Return Speed
 Influence of Coil Overheating on Continuous Duty of 2-Way Solenoid Valve
Influence of Coil Overheating on Continuous Duty of 2-Way Solenoid Valve
 PVC Flexible Tubing vs PU Tubing: Cost Difference Analysis in Equipment Internal Routing
PVC Flexible Tubing vs PU Tubing: Cost Difference Analysis in Equipment Internal Routing
 The principle and characteristics of vacuum generators
The principle and characteristics of vacuum generators
You May Interest In




Dec 06, 2025 Blog
How to check pneumatic solenoid valve?

Dec 04, 2025 Blog
How does a single solenoid valve work?
Dec 03, 2025 Blog
What is double acting solenoid valve?
Dec 02, 2025 Blog
How to clean a pneumatic solenoid valve?
Nov 30, 2025 Blog
How to select pneumatic solenoid valve?
Nov 29, 2025 Blog
Operational Mechanism of Pneumatic Solenoid Valves

Nov 27, 2025 Blog
What is pilot operated solenoid valve?




Links: www.fescolo.com(Pneumatic)
FOKCA ©1998-2025 All Rights Reserved Sitemap