Dec 09, 2025
Direct-acting solenoid valves are essential components in modern fluid control systems. They are valued for their simple structure, fast response, and ability to work reliably without any minimum pressure difference. Unlike pilot-operated types, a direct-acting valve uses only electromagnetic force to move the plunger and control the flow, making it suitable for low-pressure and zero-pressure conditions.
Understanding their structure and operation helps engineers choose the right valve and allows operators to troubleshoot and maintain the system more effectively. This article will briefly explain the internal design, working principle, and typical applications of direct-acting solenoid valves.
Direct-acting solenoid valves, also known as zero-rated solenoid valves, are simply solenoid valves that can directly open or close without relying on pipeline pressure differences. When energized, the electromagnetic force directly pulls the valve core; when de-energized, a spring returns the valve core to its original position. They are simple in structure, have a fast response, and are suitable for low-flow, low-pressure, or vacuum systems.

◆ Suitable for operation in zero-pressure, negative-pressure, and low-pressure environments.
◆ Fast response speed.
◆ The switching action is very rapid, making them ideal for applications requiring frequent opening and closing.
◆ Simple structure and good stability.
◆ With few internal parts and no pilot structure required, Fokca solenoid valves require almost no maintenance.
◆ Compact size and easy installation.
◆ The compact design is suitable for equipment with limited installation space.
◆ Lower flow rate and limited pipe diameter
◆ Lower upper pressure limit
◆ Higher power consumption and noticeable coil heating
◆ Unsuitable for high-viscosity media
Low-pressure or pressureless systems
Medical and laboratory equipment
Small automation equipment
Home appliances and consumer electronics
Small flow loops in industrial control systems
Compared to pilot-operated solenoid valves, the biggest advantage of direct-acting solenoid valves is their ability to operate freely in pressureless or low-pressure environments. They offer fast response, simple structure, and easy maintenance, making them particularly suitable for small flow, small diameter, vacuum, medical, laboratory, and light industrial equipment.
Direct-acting solenoid valves rely on the electromagnetic force generated by a coil to directly actuate the valve core, achieving opening and closing without requiring a system pressure differential.
Working Steps:Direct-acting solenoid valves require a continuous power supply during their operation.
When the coil is energized:
The coil generates magnetic force.
The magnetic force directly pulls up the valve core (piston).
The valve opens, and the medium begins to flow.
When the coil is de-energized:
The magnetic force disappears.
The spring pushes the valve core back to its original position.
The valve closes, and the medium stops flowing.
A solenoid valve is an actuating component that uses electromagnetic force to control the opening and closing of the valve core. It is a key element in pneumatic systems for controlling airflow direction, flow rate, and pressure. For precise pneumatic control and reliable solenoid valve solutions, trust FOKCA.
www.siemens.com:Industrial automation products
www.parker.com:Pneumatic and hydraulic components
www.festo.com:Pneumatic components manufacturer
www.nidec.com:Manufacturer of various motors, including fan motors, servo motors, and stepper motors
www.isa.org:Technical training and conferences in the automation industry
www.kuka.com:Industrial robots
(9016)
 Globe Valve Installation Direction Errors and Corrosion Risks You Can’t Ignore
Globe Valve Installation Direction Errors and Corrosion Risks You Can’t Ignore
 Limitations of Globe Valves in Low-Pressure, High-Flow Systems
Limitations of Globe Valves in Low-Pressure, High-Flow Systems
 ED Seal vs O-Ring in Flat Sealing Systems: Which Delivers Better Sealing Performance
ED Seal vs O-Ring in Flat Sealing Systems: Which Delivers Better Sealing Performance
 Why Hydraulic Quick Couplers Are More Prone to Seepage Under High Pressure
Why Hydraulic Quick Couplers Are More Prone to Seepage Under High Pressure
 Installation Considerations for Angle Seat Valves in Vertical and Horizontal Pipelines
Installation Considerations for Angle Seat Valves in Vertical and Horizontal Pipelines
You May Interest In



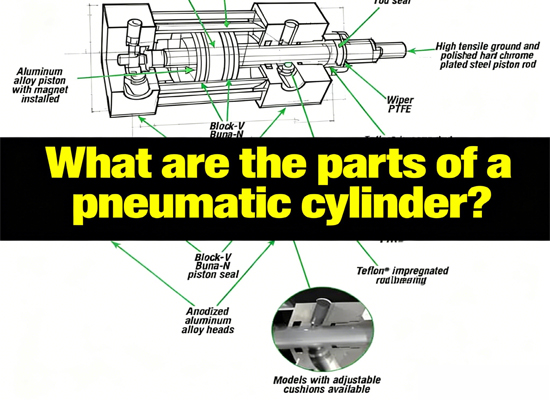
Dec 02, 2025 Blog
What are the parts of a pneumatic cylinder?












Apr 18, 2025 Blog
What is an Angle Seat Valve?Links: www.fescolo.com(Pneumatic)
FOKCA ©1998-2025 All Rights Reserved Sitemap