Jul 16, 2025
Pneumatics is a technology that studies and applies the transmission and control of energy using compressed air.For example, after mold forming, the parts need to be removed, and the continuous extension and retraction of the pneumatic cylinder piston rod can be utilized; pneumatic screwdrivers can replace manual screwing in the assembly of electronic products, home appliances, and automotive parts, providing faster speed and controllable torque.
Pneumatic products use compressed air to transmit power through various interconnected components, ultimately achieving controlled motion or performing execution functions within the pneumatic system.
A pneumatic system is made up of a variety of basic pneumatic components that feature simple structures and clean energy, and they are widely used in industries that require rapid response and repetitive operations,Each pneumatic device functions as a pneumatic system and is an application form of pneumatic technology.To help you understand the composition and working principle of pneumatic systems more systematically, this article will introduce six common example of pneumatic devices and provide detailed information on the roles each component plays in pneumatic systems.
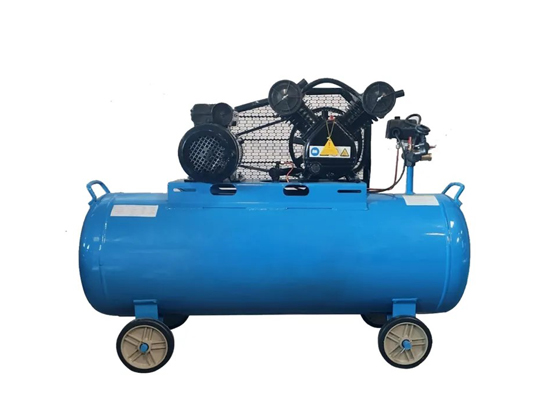
The air compressor is the primary energy supply device in a pneumatic system.The air compressor is typically a kind of basic power source supply system component Increase air pressure that located at the front end of a pneumatic system, followed by the air storage tank and air treatment unit.To allow compressed and purified air to enter the control system and actuators,It enables pneumatic technology to have the power.
As the power source of the pneumatic system, the main function of the air compressor is to compress atmospheric air into high-pressure air, store it in the air tank, or deliver it through pipelines to various products of the pneumatic system, providing a continuous and stable energy source for actuators such as air cylinders.
To ensure proper and effective use of the air compressor and to reduce future maintenance costs, the following operating procedures and precautions should be followed:
Operating Instructions:
Check whether the lubricating oil is sufficient;
Ensure the power connection is secure;
Check that the exhaust valve and drain valve are closed;
Start the compressor in unloaded mode and wait until it runs smoothly before loading;
Set the pressure range; the common pressure range for pneumatic systems is 0.5–0.8 MPa;

Precautions During Operation:
Air cleanliness: Air with impurities will affect the service life of pneumatic components. Use a filter-regulator-lubricator (FRL) unit to filter, regulate, and lubricate the air.
Pipeline layout: Design pipelines to be as short and straight as possible to minimize pressure loss and air leakage.
Pipe diameter selection: Select pipe diameters appropriate to the pressure range to avoid pressure instability.
Air tank capacity: The capacity should match the system's air consumption, typically 6–10 times the total exhaust volume.
Compressed air pressure: Must not exceed the minimum rated pressure of any pneumatic component.
Moreover:
It is recommended to use compressors or air tanks with automatic drainage functions;
Regularly maintain the compressor;
For high-demand applications, oil-free compressors and precision filtration equipment should be used.
Air source units are fundamental components of the compressor air supply process system that commonly referred to as FRL units (Filter, Regulator, Lubricator), and are responsible for purifying compressed air from air compressor. They are typically installed between the air compressor and pneumatic valves. These three components are usually integrated into a single module for convenient installation and maintenance. FRL make the pneumatic technology have clean power.
Equipped with an internal filter element and drainage device, the filter removes solid particles and liquid water as the air passes through. This process eliminates moisture, dust, and other contaminants from compressed air, protecting downstream pneumatic components.
The regulator adjusts outlet pressure via an internal spring and diaphragm mechanism, ensuring the compressed air is regulated to a stable working pressure required by the system. This guarantees safe and efficient operation.
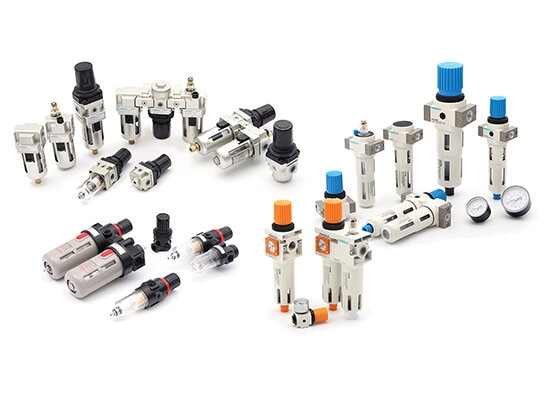

The lubricator atomizes lubricating oil through a nozzle and mixes it evenly into the airflow, providing necessary lubrication to pneumatic components. This reduces friction and wear, thereby extending equipment life.These components are not only used in pneumatic systems but also offer advantages in spray painting equipment, food processing industries, and other applications.
Air valves are fundamental components of pneumatic control systems. Their primary function is to deliver compressed air—processed by the air preparation unit—to the actuator system. The main operating steps include on/off control, flow rate regulation, and air distribution. Essentially, they distribute the air supply to different actuators according to the control signals from the system. Air valves are a key element in enabling automation through pneumatic technology.
Regularly check and replace the filter element to prevent clogging, which may lead to pressure drops or degraded air quality;
Adjust the pressure regulator to the appropriate operating pressure range to avoid excessive or insufficient pressure;
Refill lubricating oil regularly to prevent dry friction, which can cause damage to cylinders or valves;
Select suitable filtration grades and lubricant types based on the working environment;
Purchase from qualified pneumatic product manufacturers who offer stable and reliable product quality, as well as pre-sales support and technical services.
You can continue reading about topics very related to this article,such as pneumatic control system and valve, pneumatic hoses and fittings.You also can browse more of our article series for more information about pneumatic products.
 Why Quick Exhaust Valves Are Needed in Pneumatic Systems
Why Quick Exhaust Valves Are Needed in Pneumatic Systems
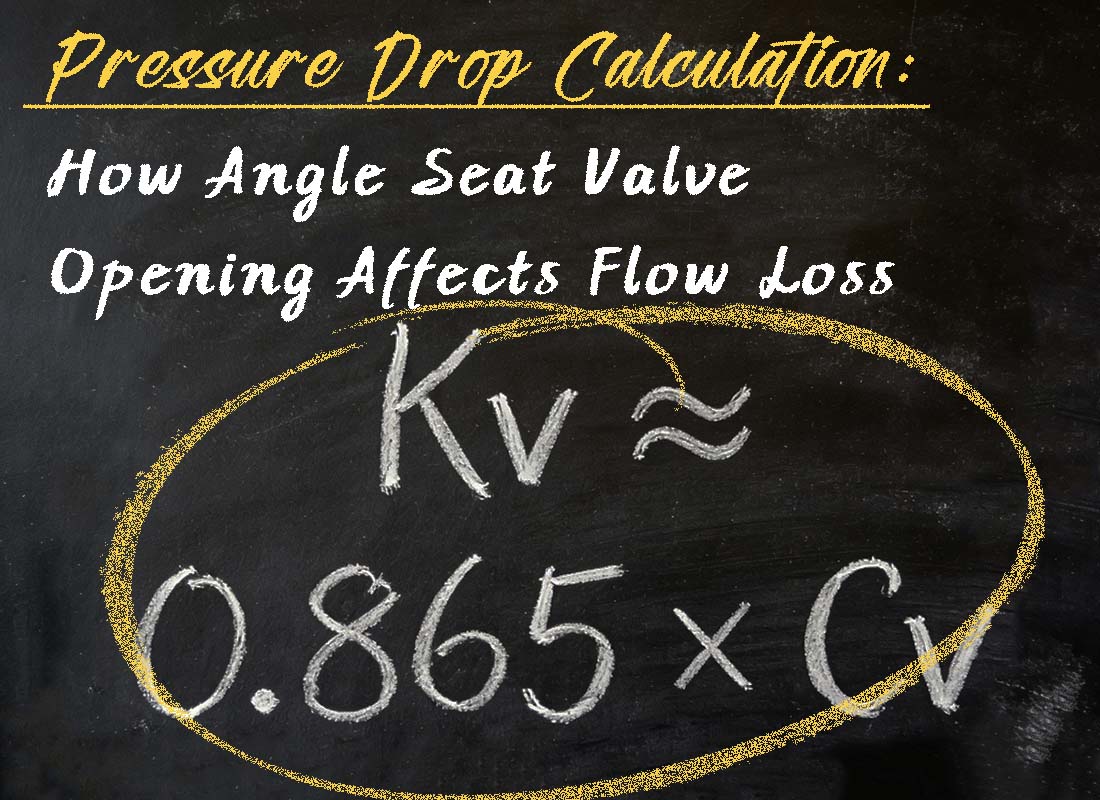 Pressure Drop Calculation: How Angle Seat Valve Opening Affects Flow Loss
Pressure Drop Calculation: How Angle Seat Valve Opening Affects Flow Loss
 IP Protection Rating of Solenoid Valve Coils
IP Protection Rating of Solenoid Valve Coils
 Can PP Polypropylene Tube Replace Certain Metal Piping in Low-Pressure Systems
Can PP Polypropylene Tube Replace Certain Metal Piping in Low-Pressure Systems
 UV Resistant Polyurethane Tubing vs PVC Tubing for Outdoor Applications
UV Resistant Polyurethane Tubing vs PVC Tubing for Outdoor Applications
You May Interest In


Nov 12, 2025 Blog
What is a single acting cylinder?
Nov 06, 2025 Blog
Why choose a single acting pneumatic cylinder?
Links: www.fescolo.com(Pneumatic)
FOKCA ©1998-2025 All Rights Reserved Sitemap