Jun 24, 2025
Pneumatic systems are very common in our daily lives, and the compressed air that flows through these systems often requires precise management and control. To achieve accurate air control within a pneumatic system, it is essential to invest in specialized control valves that regulate the flow, pressure, and direction of the gas medium. Pneumatic solenoid valves, as key pneumatic components for controlling airflow, are specifically designed to meet such high demands. They enable efficient management of actuators, cylinders, and various automation devices. Whether in manufacturing, food processing, medical equipment, or DIY automation projects, it is crucial to choose the best pneumatic solenoid valve for automation to ensure system performance and stability.
Therefore, it becomes necessary to understand how a pneumatic solenoid valve works and how to use pneumatic solenoid valves to optimize airflow systems across different industries.
This article will explore pneumatic solenoid valves in detail. It will introduce the advantages of pneumatic directional control valves and provide information on various configurations available on the market. By the end, you will have all the necessary information to make a well-informed and balanced decision when selecting valves for various airflow applications.
There are various types of pneumatic solenoid valves available on the market today. Before selecting a specific valve for a particular pneumatic application, it is important to understand the function and naming conventions of each valve. The names of pneumatic solenoid valves are based on the number of ports, positions, and flow paths. These valve positions and ports determine the range of functions a valve can perform. Below is an explanation of each term and its application in pneumatic solenoid valves:
Port – Refers to the openings or connection points on the valve body. These openings can serve as the inlet or outlet of the pneumatic solenoid valve, allowing compressed air to flow through.
Position – The valve's position refers to the state of the flow path or passage. Positions determine how different compressed air pathways are connected or restricted. Certain valve positions allow air to flow through the valve ports, while others block the airflow.
Way – These are the existing flow directions or predefined paths that compressed air can follow when passing through the pneumatic solenoid valve.
Valve types range from simple to complex multi-position and multi-port configurations, such as 2-way 2-position, 3-way 2-position, 5-way 2-position, and more complex 5-way 3-position valves. We will now introduce the characteristics of each pneumatic component type one by one.
Whether it's a 2-way 2-position solenoid valve or a 3-way 2-position solenoid valve, their common feature is having two states: energized (open) and de-energized (closed). The 3-way 2-position valve adds an internal exhaust function on top of that.
2-Way 2-Position Valve:
When energized: Opens → Air flows from the inlet port to the outlet port (one-way flow)
When de-energized: Closes → Fluid is blocked and cannot pass through
This functions like a simple "door switch," only allowing for "on" or "off" states.
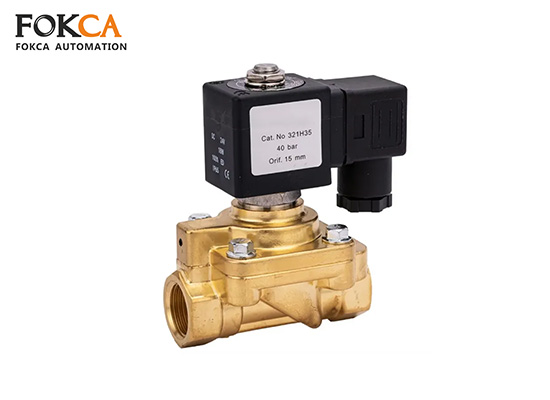

3-Way 2-Position Valve:
When energized: Air flows from the inlet port to the working port, and the exhaust port is closed
When de-energized: The working port is connected to the exhaust port, and the inlet port is closed
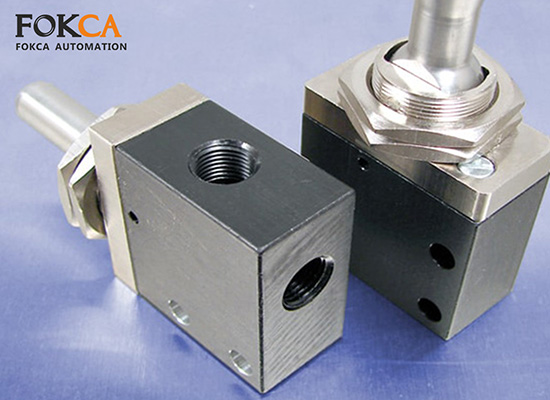

2-Way 2-Position Valves are used for simple on/off air supply control or where the goal is simply to start or stop the flow of air or fluid.
2-Way 3-Position Valves are used to control single-acting cylinders or other actuators that include a return spring and require controlled exhaust.
What Are the Features of 2-Position 5-Port and 3-Position 5-Port Solenoid Valves?
5-port solenoid valves have a more complex structure, typically featuring:
1 inlet port
2 outlet ports
2 exhaust ports

3-Position 5-Port Solenoid Valves have an additional center position compared to the 2-position variant. In the de-energized or default state, this center position can take on different functional configurations:
Closed Center: All ports are closed → The A/B sides of the cylinder are sealed, maintaining pressure and holding the piston position.
Exhaust Center: All ports are open to exhaust → No pressure on either side of the cylinder, allowing the piston to move freely.
Pressure Center: Both A and B ports are connected to the pressure supply → Cylinder is pressurized on both sides, keeping the piston in a balanced, non-moving state.

Precise Control
Fast Response
Durability and Reliability
Energy Efficiency
Safety
Automated Production Lines: Used to control robotic arms, feeders, clamps, and other devices to improve production efficiency
Packaging Machinery: Provides precise control of cylinder movements during labeling, filling, sealing, and other processes
Food and Beverage Processing: Ideal for environments requiring high-speed cleaning and frequent start-stop operations
Homemade Robots or Robotic Arms: Enables actions like gripping and pushing via simple PLC or Arduino control
Automatic Doors / Flip-Lid Systems: Used for remote-controlled pneumatic access or automated enclosure openings
Pneumatic Lifting Platforms: Suitable for desktop adjusters, projectors, monitor stands, etc.
Air Cannons and Pneumatic Toys: Creative experiments or pneumatic entertainment devices that are both functional and fun
◆ Valve Type & Configuration
◆ Flow Rate & Port Size
◆ Voltage Selection
◆ Response Time
◆ Material Compatibility
◆ Environmental Conditions
◆ Mounting & Installation Method
◆ Brand Recommendations
Choosing the appropriate pulmonary aerosol valve for you needs to consider the above important factors.
To ensure optimal performance and reduce future maintenance costs, follow these recommendations for the installation and upkeep of solenoid valves:
Confirm Flow Direction: Before installation, carefully check the airflow direction indicated on the valve body (usually marked with an arrow). Make sure the inlet, outlet, and exhaust ports are correctly connected.
Keep Components Clean: Thoroughly blow out all pipelines and fittings before installation to prevent dust and metal debris from entering the solenoid valve and causing blockages.
Secure Mounting: Use appropriately sized screws or mounting brackets to ensure the solenoid valve is firmly fixed in place and won’t loosen due to vibration during operation.
Match Voltage: Ensure the power supply voltage matches the rated voltage of the solenoid valve to avoid burning out the coil.
Use Dry Air: If driven by compressed air, it is recommended to install an air dryer and filter to prevent moisture and oil contamination from entering the system.
Regular Cleaning: Clean the exterior of the solenoid valve every 3 to 6 months, and check for any foreign objects blocking the ports.
Monitor Response Time: Observe the valve switching action. It should be quick and smooth. Delayed or sluggish response may indicate coil aging or internal carbon buildup.
Test the Solenoid Coil: Use a multimeter to check the coil’s resistance to avoid control failure due to a burnt-out coil.
Replace Seals Periodically: Regularly replace consumable components such as O-rings and gaskets to prevent leakage.
Lubrication and Care: For certain models, periodically apply specialized pneumatic lubricating oil to maintain internal flexibility.
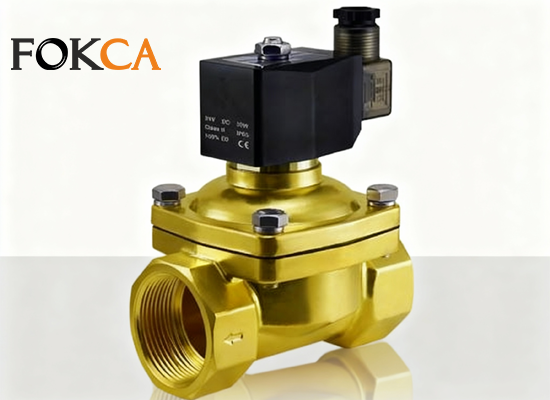
A solenoid valve is a pneumatic control component that controls airflow using an electric signal. When energized, the coil generates a magnetic field that shifts the valve spool to change the airflow path; when de-energized, the spool returns to its original position.
Common operating voltages include DC 24V, AC 110V, and AC 220V. Always match the power supply to the valve's specifications.
2-way 2-position
3-way 2-position
5-way 2-position / 5-way 3-position
A high-quality solenoid valve can perform millions of switching cycles. Its actual lifespan depends on usage frequency, air quality, and maintenance practices.
 Globe Valve Installation Direction Errors and Corrosion Risks You Can’t Ignore
Globe Valve Installation Direction Errors and Corrosion Risks You Can’t Ignore
 Limitations of Globe Valves in Low-Pressure, High-Flow Systems
Limitations of Globe Valves in Low-Pressure, High-Flow Systems
 ED Seal vs O-Ring in Flat Sealing Systems: Which Delivers Better Sealing Performance
ED Seal vs O-Ring in Flat Sealing Systems: Which Delivers Better Sealing Performance
 Why Hydraulic Quick Couplers Are More Prone to Seepage Under High Pressure
Why Hydraulic Quick Couplers Are More Prone to Seepage Under High Pressure
 Installation Considerations for Angle Seat Valves in Vertical and Horizontal Pipelines
Installation Considerations for Angle Seat Valves in Vertical and Horizontal Pipelines
You May Interest In



Dec 02, 2025 Blog
What are the parts of a pneumatic cylinder?












Apr 18, 2025 Blog
What is an Angle Seat Valve?Links: www.fescolo.com(Pneumatic)
FOKCA ©1998-2025 All Rights Reserved Sitemap