Oct 16, 2025
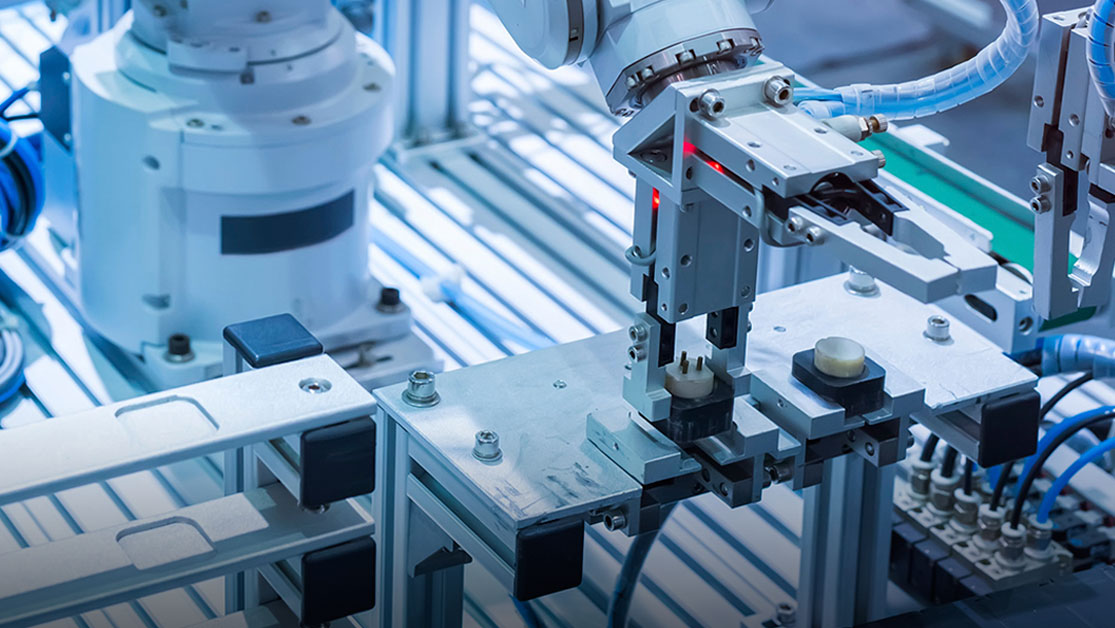
On the electronics production line, the smart pneumatic automatic assembly machine used for assembling switch modules is a typical application of a pneumatic air-operated machine.
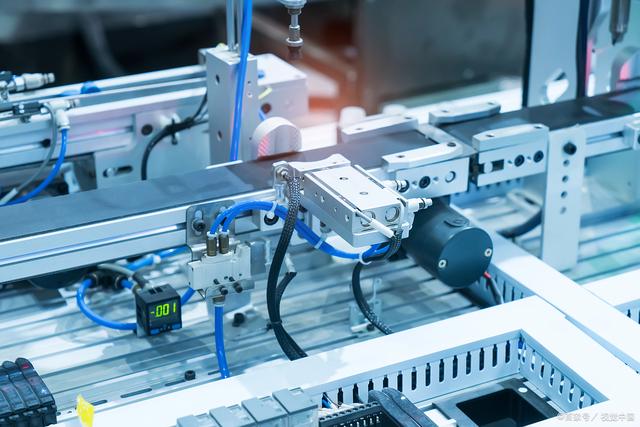
The neatly arranged parts in the hopper are first transported to the conveyor track by a pneumatic vibratory feeder or a feeding cylinder. When a part slides into the assembly position, a limit sensor detects that the part is in place and sends the signal back to the PLC system. Then, a pneumatic fixture driven by a double-acting cylinder gently clamps the part, securing it in the precise position. Once the part is correctly positioned, an optical sensor triggers the pneumatic stamping cylinder to operate, pushing the punch to accurately insert the switch module into the plastic housing. The PLC controls the entire sequence of actions: first clamping, then stamping, holding the pressure for a certain time, and finally retracting slowly.
After assembly, sensors automatically inspect the assembled components to confirm whether the switch module is fully in place.
A pneumatic machine is not a pneumatic device that performs a single action or function. Instead, it can carry out more complex and diversified system operations and functions, often involved in the processing or manufacturing of a finished product. The associated commands and mechanical actions are usually also diverse. For example, the automatic assembly of switch modules requires multiple pneumatic actuators and various sensors for state and position detection, all of which need a control system to coordinate.
By combining multiple pneumatic devices with control logic, a pneumatic machine can form a complete operational workflow. Its components include:A more complete set of pneumatic handling preparation components includes multiple pneumatic elements or actuators, centralized solenoid valves for more effective distribution and control of large volumes of compressed air, and more efficient transmission piping and sealing accessories.
Pneumatic strapping machine: Used for automatically sealing or bundling cartons or products.
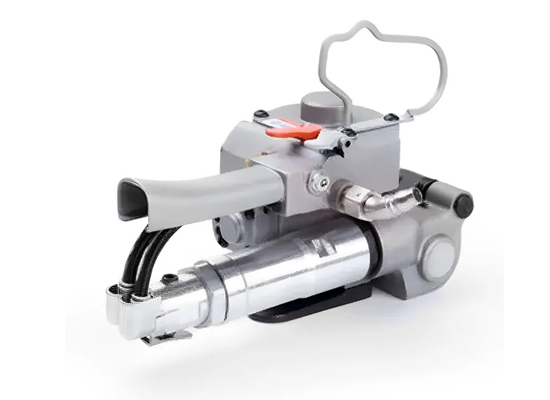

Pneumatic can crusher: Automatically crushes canned products in the food processing industry.
Pneumatic punch press: Performs stamping or punching on hardware or plastic parts.
Pneumatic fixture: Automatically clamps or handles workpieces, used on assembly lines or as robot end-effectors.
◆ Integration with electrical control and imaging/digital sensing technologies
◆ Smarter pneumatic systems
◆ Low-energy consumption and green design
◆ Efficient transmission of energy using compressed air to reduce energy consumption
◆ Modular design and IoT monitoring
◆ Real-time monitoring of air pressure, air consumption, and fault information
 The principle and characteristics of vacuum generators
The principle and characteristics of vacuum generators
 Action Delay of 2-Way Solenoid Valve in Long-Pipe Installation
Action Delay of 2-Way Solenoid Valve in Long-Pipe Installation
 Pilot Orifice Blockage: Hidden Risk in Micro Passages of Solenoid Valve
Pilot Orifice Blockage: Hidden Risk in Micro Passages of Solenoid Valve
 Pneumatic Vacuum Filter: Design Differences between SMC Type and Common Filters
Pneumatic Vacuum Filter: Design Differences between SMC Type and Common Filters
 Why Your PU Tube Burst? The Truth About Temperature & Pressure
Why Your PU Tube Burst? The Truth About Temperature & Pressure
You May Interest In



Dec 02, 2025 Blog
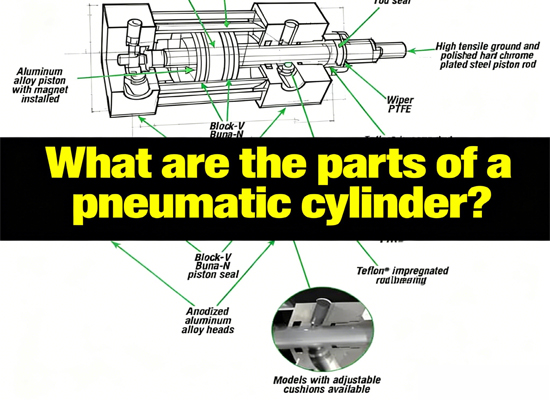
What are the parts of a pneumatic cylinder?












Apr 18, 2025 Blog
What is an Angle Seat Valve?Links: www.fescolo.com(Pneumatic)
FOKCA ©1998-2025 All Rights Reserved Sitemap