Feb 05, 2026
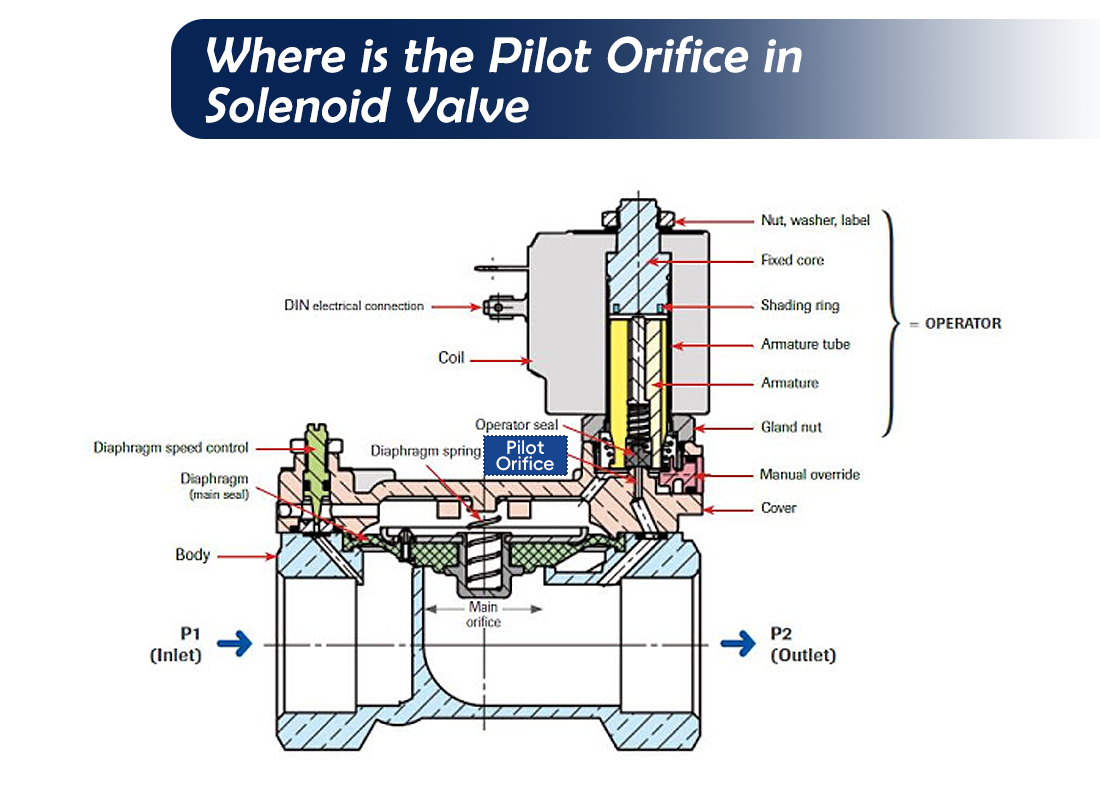
In a solenoid valve, the coil is only part of the story. The tiny pilot orifice actually determines whether the valve can move correctly. When energized, the core opens this passage and releases pressure from the control chamber, allowing the main spool to shift. When power is removed, pressure builds again and the valve closes. This mechanism means that the valve relies on pressure balance rather than pure magnetic force. If the orifice becomes restricted, the valve may fail even though the electrical components remain healthy. Many field engineers encounter this situation after replacing coils with no improvement.
Real industrial media always contain impurities. Rust particles, seal debris and oil mist travel through the pipeline and enter the valve body. In a pneumatic solenoid valve or pilot solenoid valve, these contaminants easily adhere to the micro passage and reduce its diameter. The first symptom is longer opening time, followed by incomplete closing and finally total malfunction. A direct acting solenoid valve is more tolerant because it does not rely heavily on differential pressure. This difference explains why identical working conditions may produce completely different reliability results.
| Valve type | Dependence on pilot orifice | Sensitivity to particles | Typical symptom |
|---|---|---|---|
| Direct acting solenoid valve | Low | Medium | Coil overload |
| Pilot solenoid valve | High | High | Delayed opening |
| Industrial solenoid valves | Varies | Medium–High | Unstable flow |
| High speed solenoid valve | High | Very high | Missed action |
This table reflects numerous maintenance records from automation plants and equipment manufacturers.
In applications such as solenoid valve in HVAC systems, temperature fluctuation produces condensate inside the housing. Water mixed with fine dust forms sticky deposits that gradually block the pilot path. Users often believe the problem is electrical, but the real cause is mechanical obstruction. For solenoid valve for compressed air, inadequate air preparation dramatically shortens service life. Proper drying and filtration are as important as selecting a quality valve.

During selection, engineers should evaluate cleanliness level before choosing structure. In contaminated environments, a solenoid valve manifold with integrated filtration is safer. Modern factories can use an automated solenoid valve control system to monitor cycle data and detect abnormal delay. Regular solenoid valve maintenance and troubleshooting should include checking response time and cycle life instead of only measuring coil voltage. Many valves return to normal performance after simple flushing of the pilot channel.
For distributors and purchasers, pilot orifice blockage represents a hidden expense. Low-price valves may create frequent downtime and service calls, while a properly designed product ensures long-term stability. Recognizing how this micro passage works helps users make rational decisions and protect the whole automation system. The reliability of a large production line often depends on this small detail inside the solenoid valve.
(FK9025)
 Action Delay of 2-Way Solenoid Valve in Long-Pipe Installation
Action Delay of 2-Way Solenoid Valve in Long-Pipe Installation
 Pilot Orifice Blockage: Hidden Risk in Micro Passages of Solenoid Valve
Pilot Orifice Blockage: Hidden Risk in Micro Passages of Solenoid Valve
 Pneumatic Vacuum Filter: Design Differences between SMC Type and Common Filters
Pneumatic Vacuum Filter: Design Differences between SMC Type and Common Filters
 Why Your PU Tube Burst? The Truth About Temperature & Pressure
Why Your PU Tube Burst? The Truth About Temperature & Pressure
 Temperature Difference: Influence of Condensation on Solenoid Valve Reliability
Temperature Difference: Influence of Condensation on Solenoid Valve Reliability
You May Interest In



Dec 06, 2025 Blog
How to check pneumatic solenoid valve?

Dec 04, 2025 Blog
How does a single solenoid valve work?
Dec 03, 2025 Blog
What is double acting solenoid valve?
Dec 02, 2025 Blog
How to clean a pneumatic solenoid valve?
Dec 01, 2025 Blog
How to Wire and Install a Pneumatic Solenoid Valve?
Nov 30, 2025 Blog
How to select pneumatic solenoid valve?
Nov 29, 2025 Blog
Operational Mechanism of Pneumatic Solenoid Valves

Nov 27, 2025 Blog
What is pilot operated solenoid valve?




Links: www.fescolo.com(Pneumatic)
FOKCA ©1998-2025 All Rights Reserved Sitemap