Dec 04, 2025
A single solenoid valve is a type of valve that uses an electromagnetic coil to control the flow of air, gas, or liquid in a system. It is widely used in automation and fluid control applications due to its simple structure, fast response, and reliable on/off operation.
Single-acting solenoid valves are used in both pneumatic and hydraulic systems due to their simple structure and low cost. Solenoid valves with a more robust structure and stronger pressure resistance, used in hydraulic systems, are called single-acting hydraulic solenoid valves; similarly, solenoid valves with weaker pressure resistance, used in pneumatic systems, are called single-acting pneumatic solenoid valves.
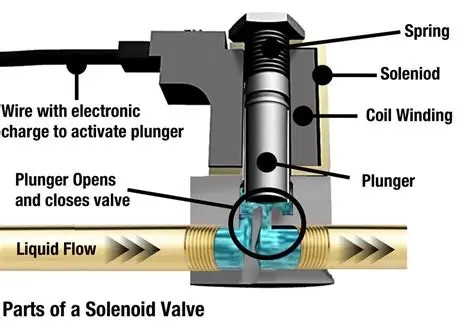
To understand how it works, we first need to learn about its key parts:
Coil: An electromagnet that generates a magnetic field when energized.
Valve Core/Plunger: A movable metal rod inside the coil that is attracted by the magnetic force.
Spring: Provides a force opposite to the electromagnetic force, used to reset the valve core.
Valve Orifice: The opening through which fluid (air, water, oil, etc.) flows.
Seal: Typically attached to the valve core, used to open or close the valve orifice.
The operation of a single-acting solenoid valve is not complicated; it will be explained in two main states.
No power supply: The coil is not powered, and the electromagnet does not work.
Spring force action: The spring is in an extended or natural state, pushing the valve core downwards.
Sealed closure: The valve core tightly presses the seal onto the valve port, blocking the fluid passage.
Result: The valve is in the closed state. The fluid cannot flow from the inlet (P) to the outlet (A).
Electrification: When current passes through a coil, a strong magnetic field is generated.
Electromagnetic force effect: Magnetic force will attract the valve core and overcome the spring force to move upward.
Spring compression: The movement of the valve core compresses the spring.
Seal opening: The valve core is lifted, driving the seal away from the valve port and opening the fluid channel.
Result: The valve is in the open state. The fluid can now flow freely from the inlet (P) to the outlet (A).
Advantages:
Simple and reliable structure: few parts, low failure rate, and low cost.
Fault safety: It can automatically restore to the default state when power is cut off, with high safety.
Low energy consumption: Usually only consumes electricity when changing state (in one direction).
Disadvantages:
Spring limitation: Electromagnetic force must overcome spring force, which limits the working pressure range of the valve and is usually not suitable for ultra-high pressure applications.
Single function: can only control one action. For devices that require precise control of two directional movements (such as double acting cylinders), dual electronic control solenoid valves are required.
Single-acting solenoid valves are widely used in applications that require simple on/off control:
Irrigation systems: Controlling the flow of water.
Household appliances: Water inlet valves for washing machines and dishwashers.
Industrial automation: Controlling single-acting cylinders.
HVAC systems: Managing the flow of refrigerants and water.
Medical equipment: Precisely regulating the flow of gases and liquids.
Water purifiers and coffee machines: Controlling water intake.
Other manufacturing-related websites as below:
www.crossco.com:Industrial automation and integrated system/services
www.ethercat.org:A company specializing in industrial flexible cables
www.igus.com:Infrastructure development for communication and control systems in robots, production lines, machine tools, and automation equipment
www.manufacturing.net:Hoses, pneumatic components, cables, and sensors
www.motoman.com:Industrial robots and fully-integrated robotic automation systems.
www.cc-link.org:industrial network protocols / automation networks
(9016)
 Impact of Trapped Media in the Valve Cavity on Restart Performance of Pneumatic Ball Valves
Impact of Trapped Media in the Valve Cavity on Restart Performance of Pneumatic Ball Valves
 Wear Path Analysis of Pneumatic Ball Valve Under Frequent Cycling Conditions
Wear Path Analysis of Pneumatic Ball Valve Under Frequent Cycling Conditions
 Mini Push In Fittings: Aging Problems of Plastic Bodies in Humid Environments
Mini Push In Fittings: Aging Problems of Plastic Bodies in Humid Environments
 Mini Type Pneumatic Push In Fittings: Flow Difference Between Straight and Elbow Designs
Mini Type Pneumatic Push In Fittings: Flow Difference Between Straight and Elbow Designs
 Influence of Exhaust Throttling of 3-Way Solenoid Valve on Actuator Return Speed
Influence of Exhaust Throttling of 3-Way Solenoid Valve on Actuator Return Speed
You May Interest In



Dec 02, 2025 Blog
What are the parts of a pneumatic cylinder?












Apr 18, 2025 Blog
What is an Angle Seat Valve?Links: www.fescolo.com(Pneumatic)
FOKCA ©1998-2025 All Rights Reserved Sitemap