Pneumatic Products Overview
Pneumatic products include air compressors, air preparation units, cylinders, pneumatic valves, pneumatic hoses, and fittings.This article focuses on three main categories:Air compressors,Air treatment units and Air cylinders.
The primary focus, however, is to introduce the advantages, disadvantages, types, and applications of:Pneumatic valves,Pneumatic tubing and fittings.
Pneumatic Valves
Pneumatic valves serve as the critical link between the control system and actuators, determining the response speed, motion logic, and overall stability of a pneumatic system. Choosing high-performance pneumatic valves can not only enhance the level of automation but also extend system lifespan and reduce maintenance costs.
Functioning as the "command center" of a pneumatic system, pneumatic valves primarily control the direction, pressure, and flow of compressed air to precisely manage the actions of cylinders or actuators. The controlled media may include compressed air, steam, or liquids.
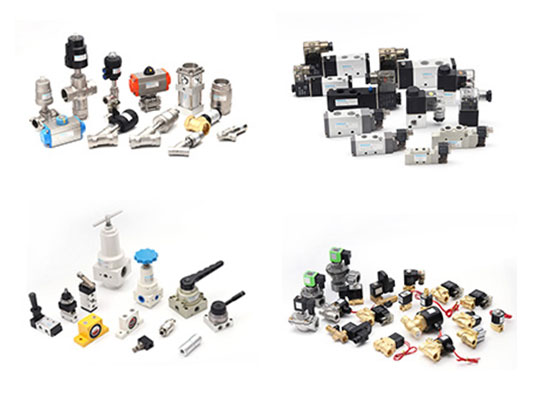

Types of Pneumatic Valves and Their Functions
Angle Seat Valve:This type of angle seat valve is used for fast on/off switching of the system medium and is suitable for high-temperature or high-viscosity media.
Globe Control Valve: Offers precise flow regulation, but with higher flow resistance and greater pressure loss.
Pneumatic Axial Valve: Controls fluid in an axial direction with fast response; ideal for rapid switching applications.
Pneumatic Ball Valve: Enables quick switching with excellent sealing performance; fast to open and close, suitable for remote automatic control.
Diaphragm Valve: Suitable for corrosive media and applications with high sanitary requirements.
Pneumatic Solenoid Valve: Allows for remote automated control and modular integration.
Pulse Solenoid Valve: Driven by pulse signals; used to control jet air in pulse-jet dust cleaning systems for periodic cleaning.
Pressure Regulating Valve: Automatically reduces and stabilizes downstream pressure, ensuring safe system operation and preventing pressure fluctuations.
Check Valve: Prevents backflow of media, ensures one-way flow, and protects equipment safety.
Safety Valve: Automatically releases pressure when it exceeds a preset value to protect equipment and pipelines from explosion or rupture.
Typically, valves control fluid media to further regulate actuator movements. These valves include solenoid valves, mechanical valves, and manual valves.Actuators can also be used to operate valves, such as pneumatic control valves, pneumatic ball valves, and pneumatic butterfly valves.
Which components are combined within a pneumatic flow control valve?
Common valve structures include:Valve Body,Bonnet/Cover,Plug/Ball/Disc/Diaphragm,Stem/Actuator Rod,Seals, Packing, O-rings,Ports and Actuator Mechanism.
Common types include:
"Multi-way" means the valve can connect to and control more ports, enabling more complex fluid routing. "Multi-position" means more operational states can be achieved within the system.
Another key concept is the initial state of the valve, widely used to describe the open/closed status of pneumatic, solenoid, and other automatic control valves when not powered or signaled:
Pneumatic Tubing and Fittings
Pneumatic tubing and fittings must be designed to meet the specific characteristics of pneumatic systems. The tubing is used to transport compressed air and typically operates within a pressure range of 0.4–0.8 MPa. It requires high sealing performance, smooth inner walls for efficient airflow, and seamless connection with fittings to ensure no leakage of the medium. The tubing should also be flexible enough to allow bending and twisting, while offering good wear resistance to withstand demanding environments. These properties make pneumatic tubing suitable for use in industries such as automation control, packaging, food processing, electronics, and medical equipment.

Common types and characteristics of pneumatic tubing
Tube type
| Material
| Advantages | Disadvantages
| Typical application |
| Nylon Tube | Polyamide | High strength, good pressure resistance, oil and wear resistant | Relatively rigid, large bending radius | Industrial automation, mechanical equipment |
| Polyurethane Tube | Polyurethane | Excellent flexibility, small bending radius, tear-resistant | Slightly lower pressure resistance than nylon | Robots, handling equipment, moving cylinders |
| Polyethylene Tube | Polyethylene | Low cost, lightweight, excellent chemical resistance | Low pressure resistance, poor rigidity | General low-pressure gas transmission |
| Polypropylene Tube | Polypropylene | Excellent corrosion and chemical solvent resistance | Brittle, poor impact resistance | Medical and laboratory gas transmission |
| PTFE Tube | Polytetrafluoroethylene | Outstanding temperature and corrosion resistance | Expensive, rigid | High-end chemical, pharmaceutical, bio labs |
| PVC Tube | Polyvinyl Chloride | Transparent, low cost, easy to process | Average flexibility, not heat-resistant | Non-critical auxiliary air systems |
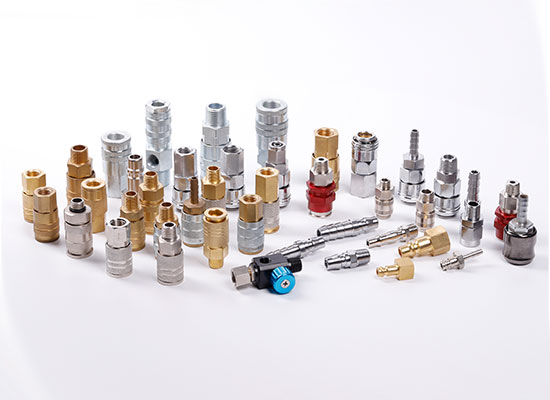
Types and characteristics of pneumatic joints
Pneumatic push in fittings
Standard pneumatic push in fitting:Generally composed of a plastic body and metal stainless steel claws, it is lightweight, quick to install, and can be automatically locked by simply inserting the trachea. Straight through, L-shaped, T-shaped, Y-shaped, threaded adapter type, etc. Widely used in industrial automation control systems, such as connecting cylinders, valves, and sensors.
Full stainless steel pneumatic one touch fitting:All materials are made of stainless steel, which has strong corrosion resistance, high strength, and high temperature resistance. The structure is sturdy and not easily deformed or aged after long-term use. It is suitable for harsh environments such as high humidity, high temperature, and frequent cleaning The price is higher than the standard quick plug connector.
Brass pipe fitting:Made of all brass material, with good pressure resistance and suitable for high-strength mechanical connections, it does not have a "quick plug" function. It is usually sealed by tightening or compressing threads, and is not suitable for frequent disassembly and assembly. It can be used for various media such as water, oil, and gas.
Nickel Plated Brass Pneumatic Push in Fitting:Brass is not corrosion-resistant. This type of joint is coated with a layer of nickel on the surface, enhancing its corrosion resistance and appearance. Compared to brass, it also has a "push in lock" quick plug function. The internal structure is similar to standard plastic quick plug joints, and common specifications include internal and external threads, L-shaped, T-shaped, suitable for medium and heavy load scenarios.
SMC standard pneumatic push in fitting:SMC products from Japan are industry standard, with high quality stability and precise craftsmanship. They are made of plastic body and metal claws, providing various structures and thread forms. They have good sealing, smooth insertion and removal, long service life, and are highly compatible with SMC cylinders, valves and other components. This brand of connector is the first choice for users who require strict requirements or are compatible with SMC systems.
Pneumatic quick coupling
Israel type pneumatic quick coupling:Metal self-locking structure, compact size
American pneumatic quick coupling:Coarse and short interface, dual plane plug, often equipped with check valve
European pneumatic quick coupling:Long plug, inclined locking, BSP thread
Japanese pneumatic quick coupling:Exquisite, slender plug, often with M or R threads
British pneumatic quick coupling:Plug length, dual structure of sealing ring, BSP thread
Hydraulic quick couling
There are various types of hydraulic joints, which can be roughly divided into the following categories:Medium-pressure hydraulic coupling,stainless steel coupling,ball valve type coupling, push and pull type coupling,flat face type coupling,thread locking coupling.
Fokca Automatic Company
Fokca Pneumatic Technology Co., Ltd. is a comprehensive enterprise specializing in the research, development, production, and sales of pneumatic components. Since its establishment, we have been committed to providing global customers with high-performance and highly reliable pneumatic solutions.
We focus on a full range of pneumatic system products, including pneumatic cylinders, cylinder accessories, pneumatic valves, air treatment units, pneumatic fittings and tubing, as well as customized pneumatic assemblies.
For more information, feel free to contact us directly.