May 21, 2025
Pneumatic control valve,as known as compressor air operated valve,Using compressed air as a driving force to control the opening or closing of valves.
In today's highly integrated and automated industrial systems, pneumatic control valve plays a pivotal role as the core components for fluid regulation. Whether the fluid is gas, liquid, or steam, pneumatic valves are essential for performing critical functions such as on-off control, flow regulation, directional control, and fluid isolation.
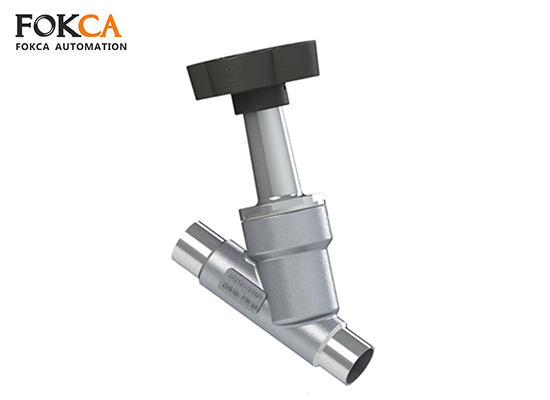

Pneumatic valve is widely used in fluid systems for industrial manufacturing, and their core functions include:
Opening and closing control: quickly cut off or connect fluid channels.
Flow regulation: achieve dynamic control of parameters such as pressure, flow rate, and temperature.
Media guidance: Changing the direction or path of the fluid to optimize the system flow.
System protection: such as check valves, explosion-proof valves, etc., to ensure system safety.
Due to the flexibility and convenience of Air operated valve, they are very practical in the field of automation industrial,Intelligent manufacturing, industrial automation.
Air operated control valve is used to regulate the flow of fluids through a series of interconnected components. These adjustments may include pipeline on/off control, fluid direction, and flow rate regulation. Before diving into how valves operate, it's essential to understand the internal structure of a valve and the functions of each valve component—this foundational knowledge provides valuable insight into the working principle of industrial valves.
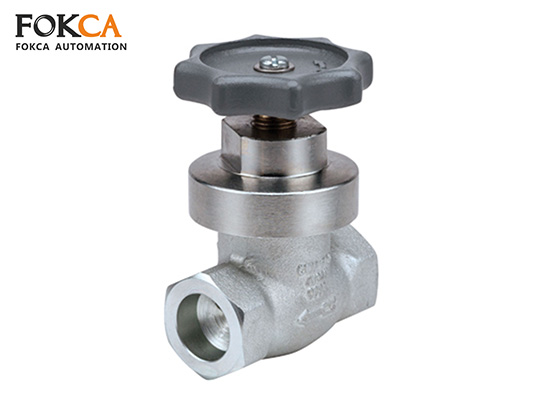

Pnuematic valve is typically composed of several core parts, each playing a specific role in fluid control systems:
Valve Body: The primary structure of the valve that houses internal components. It withstands internal pressure and connects directly to the piping system.
Valve Cover: Seals the upper part of the valve and protects internal components. It is often bolted or screwed to the valve body.
Valve Disc : The core regulating component responsible for controlling or blocking fluid flow within the valve.
Valve Seat: Provides a sealing surface for the valve disc or plug, preventing fluid leakage when the valve is closed.
Valve Stem: The actuating component that transfers motion from the actuator or handle to the valve disc, enabling opening and closing operations.
Sealing System: Includes gaskets, O-rings, and packing that prevent leaks between the valve components and ensure a tight, secure flow path.
Actuator : The external drive unit that opens or closes the valve, either manually or automatically.
Despite the diversity in valve types, the fundamental structure typically includes the valve body, bonnet, stem, disc, seat, and sealing system. This simple and user-friendly construction makes industrial valves easy to operate, maintain, and integrate into automated process control systems.
Some air operated valve may look different, but their basic working principle is similar, which is to regulate the fluid flowing through the valve body through external force.Valves play a critical role in controlling the flow of liquids, gases, and other materials in a wide range of industries. There are various types of valves designed to meet different application needs. Among the most commonly used are the angle seat valve, globe valve, and solenoid valve.
The angle seat valve is known for its durability and high flow rates because of stainless steel material and pneumatic actuator, commonly used in steam, air, and high fluid temperature applications.
The globe valve offers excellent throttling capabilities and is ideal for applications requiring precise flow regulation.
The solenoid valve operates electromechanically and is widely used for automation in fluid control systems. Due to its fast response and flexibility, the aerosol valve can also be used for respiratory systems
Other types of valves include check valves, safety valves, diaphragm valves, ball valves, etc.Each of these valves has unique characteristics and is suitable for specific industrial environments.

With the rapid advancement of Industry 4.0 and the rise of smart factory automation, traditional valve systems can no longer meet the modern demands for automated, data-driven, and intelligent process control. By integrating smart technologies, the industrial valve is evolving toward greater efficiency and intelligence, particularly in areas such as real-time monitoring, remote control, and predictive maintenance.
By embedding sensors such as pressure, temperature, and position detectors into valve systems, and using advanced devices like the pneumatic angle seat valve with positioner, engineers can achieve:
Real-time monitoring of valve opening, flow rate, and system pressure
Closed-loop control for enhanced system stability and safety
Valves such as the smart solenoid valve for PLC control and digital globe valve with feedback signal are designed to seamlessly integrate with industrial control platforms like PLC, DCS, and IoT edge devices, enabling:
Remote valve operation and centralized monitoring
Real-time status acquisition and automated process scheduling
With technologies like the predictive maintenance valve system, users can detect early signs of wear or malfunction—such as stem jamming, seal failure, or actuator drift—and take action before critical failures occur. This dramatically reduces downtime and increases maintenance efficiency.
To meet the growing complexity of smart manufacturing environments, compressor Air valve systems are now being designed for modularity and custom engineering. FOKCA offers:
Multiple connection types: threaded, flanged, or welded
Various drive mechanisms: manual, pneumatic, electric, or hydraulic
Material options for corrosion resistance, high-temperature environments, and food-grade applications
FOKCA is deeply committed to innovation in the fields of industrial automation and advanced manufacturing. We offer a full range of pneumatic products.You can visit our website to equire more information!
 Why Globe Valve Performs Better in Frequent Opening and Closing Applications
Why Globe Valve Performs Better in Frequent Opening and Closing Applications
 Rubber hose vs Polyurethane tubing vs Nylon tubing: Choosing the Right Pneumatic Hose Material
Rubber hose vs Polyurethane tubing vs Nylon tubing: Choosing the Right Pneumatic Hose Material
 How Does Mesh Affect the Performance of Pneumatic Silencers?
How Does Mesh Affect the Performance of Pneumatic Silencers?
 Hydraulic Quick Couplers: Maintenance Details Most People Overlook
Hydraulic Quick Couplers: Maintenance Details Most People Overlook
 Globe Valve Installation Direction Errors and Corrosion Risks You Can’t Ignore
Globe Valve Installation Direction Errors and Corrosion Risks You Can’t Ignore
You May Interest In

Nov 13, 2025 Blog
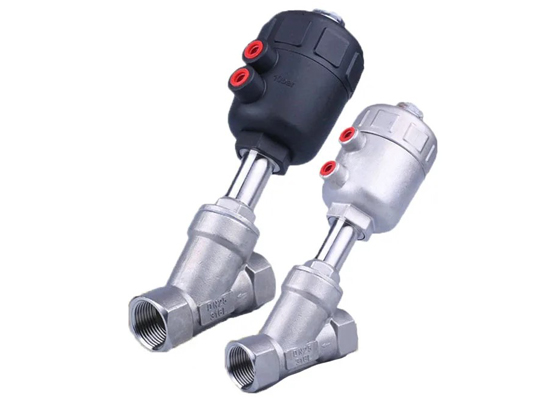
What are pneumatic angle seat valves used for?



Jul 01, 2025 Blog
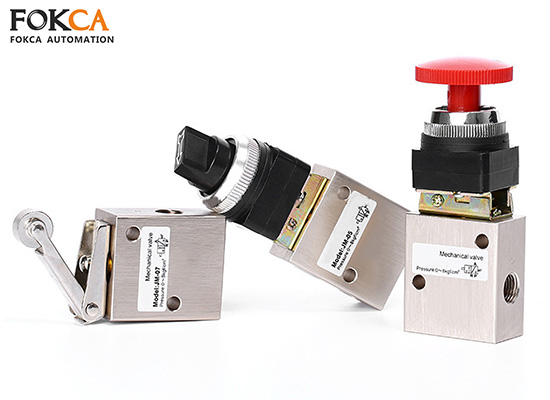
The Ultimate Guide to Mechanical Valves
Apr 18, 2025 Blog
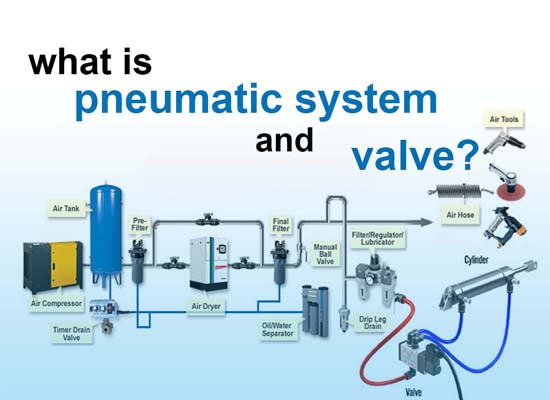
What Is Pneumatic System And Valve?Links: www.fescolo.com(Pneumatic)
FOKCA ©1998-2025 All Rights Reserved Sitemap