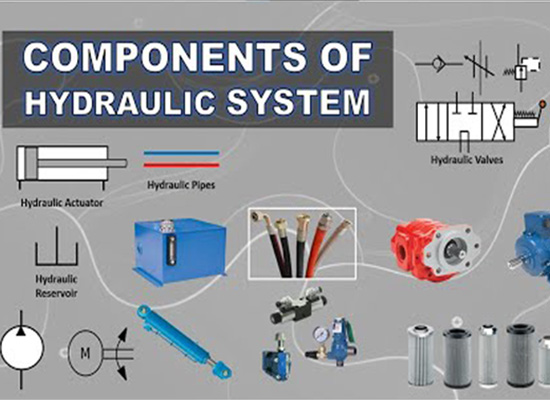
Five Core Components of a Hydraulic System
Power Components: The hydraulic pump draws low-pressure hydraulic oil from the tank, then compresses it into high-pressure, high-flow fluid and delivers it to the control components through pipes and fittings.
Control Components:The hydraulic valve delivers the regulated, direction-controlled, and speed-adjusted hydraulic oil precisely to the specified actuator through another set of pipes and fittings.
Actuating Components:High-pressure hydraulic oil enters the actuator, performs work, and then the low-pressure return oil flows back to the tank through the return pipeline system (including hydraulic pipes and hydraulic fittings).
Auxiliary Components: These support the main system efficiency and safety. Accessories include tanks, coolers, accumulators, filters, pressure gauges, hydraulic hose fittings, and more.
Working Medium: The medium under the transmission effect of hydraulic pipeline to transmit energy throughout the system while also providing lubrication, cooling, and sealing. Common media include hydraulic oil and emulsified fluids.
Hydraulic pipe fittings are connecting parts of the auxiliary types of hydraulic components. They form the hydraulic pipeline system of the hydraulic system, commonly referred to as the hydraulic transmission system or hydraulic delivery system.
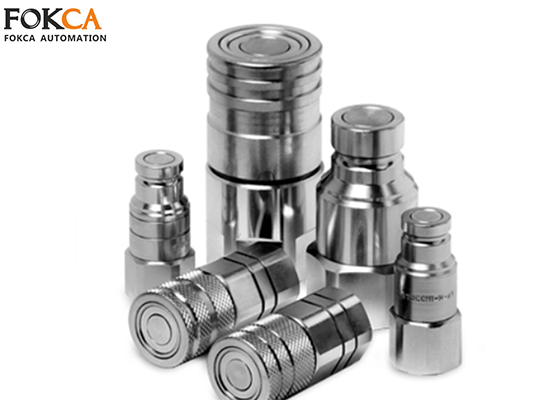

Hydraulic Piping System
The hydraulic piping system serves as the medium transmission pathway in a hydraulic system. Its primary function is to quickly and efficiently deliver hydraulic fluid between hydraulic components. Sealing performance and leak prevention are the top priorities for hydraulic piping, and it is composed of the following elements:
Hydraulic Pipes or Hoses: The hydraulic medium mainly undergoes a position change in the conveying element.
Hydraulic Fittings or Couplings: Couplings are used to connect different pipes or components to ensure sealing and safety
Quick Couplings: A specialized type of hydraulic fitting that allows for fast connection and disconnection. These are commonly used in scenarios where equipment or attachments need to be changed frequently.
Clamps, Brackets, Protective Sleeves, and Other Auxiliary Components: These elements are used to secure and protect the piping system, ensuring stable and safe operation.
With continuous industrial development, ease of operation has become an indispensable factor. Hydraulic quick couplings are an innovative type of hydraulic fitting, designed to allow quick connection and disconnection of hydraulic lines without the need for tools, making them ideal for applications requiring frequent changes or maintenance.
Hydraulic Quick Couplings
Hydraulic hose couplings are devices used for the fast connection or disconnection of hydraulic pipe. With simple operation and excellent sealing performance, they are essential components in fluid transmission systems.
Equipped with built-in locking mechanisms and sealing structures, hydraulic quick fittings ensure easy operation, safety, and reliability—making them especially suitable for applications that require frequent hose changes or disassembly.
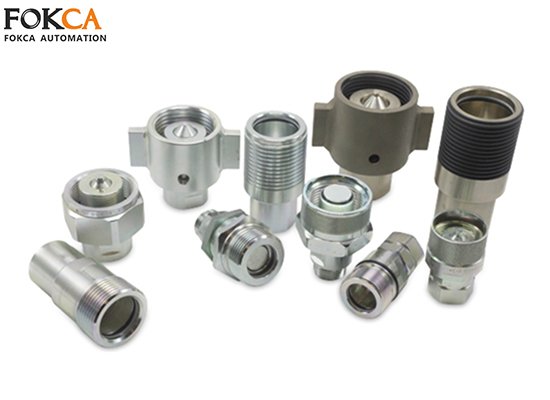

The Main Functions of Hydraulic Quick Couplings
Quick Connection and Disconnection
No tools are required during operation—simply push or pull to connect or disconnect, saving time and labor.
Leak and Contamination Prevention
The coupling automatically seals when disconnected, preventing hydraulic fluid leakage. Flat-face quick coupling designs are especially effective at keeping out air, dust, and moisture.
Enhanced System Flexibility
Commonly used in systems requiring frequent attachment changes, function expansion, or equipment mobility—such as excavator attachment swaps or agricultural implement hookups.
Classification of Hydraulic Quick Couplings
The classification of hydraulic hose fittings can be based on the connection and structural,they have various classify methods:
By Connection Method
Push-to-Connect
Simple push-in locking, commonly used in low-pressure applications and suitable for quick operations.
Screw-to-Connect
Suitable for high-pressure, high-flow, and impact load environments; provides secure connections that are not easy to loosen.
By Structural Type
Ball Valve Type
Locks using steel balls; simple structure with strong versatility.
Poppet Valve Type
Offers excellent sealing and flow control capabilities; ideal for high-pressure systems.
Flat Face
Features a flat mating surface that prevents oil leakage upon disconnection, making it especially suitable for environmentally sensitive applications such as agriculture, forestry, and construction equipment.

Common Applications Of Hydraulic Quick Couplings:
Construction machinery: excavator accessories replacement system.
Agricultural machinery: hydraulic connection between tractor and multifunctional hanging agricultural tools.
Industrial automation equipment: used for rapid installation and disassembly of hydraulic tools or actuators.
Hydraulic testing system: easy to plug and unplug for testing oil circuits and detecting pressure.
Points to Note When Selecting Hydraulic Quick Couplings
When selecting hydraulic quick fittings, the following parameters should be considered:
Working pressure
Need to match the maximum pressure of the system and reserve a safety margin
Connection size
Match with pipelines or interfaces
Flow range
Meet the system flow rate requirements and avoid pressure loss
Sealing material
Commonly used are NBR, FKM, EPDM, etc., which should be selected according to the working medium and temperature
Self proclaimed
Is the hydraulic oil automatically sealed when disconnected to prevent leakage
FAQ
Q1.What are hydraulic components
Hydraulic components are the parts that make up a hydraulic system, used to generate, control, and transmit hydraulic power. Examples include pumps, valves, cylinders, hoses, and hydraulic fittings.
Q2.How to install hydraulic fittings?
Q3.Which component creates hydraulic pressure
The hydraulic pump creates flow, and pressure is generated as the flow meets resistance in the system. So, pressure is developed by the system but initiated by the pump.