Feb 06, 2026
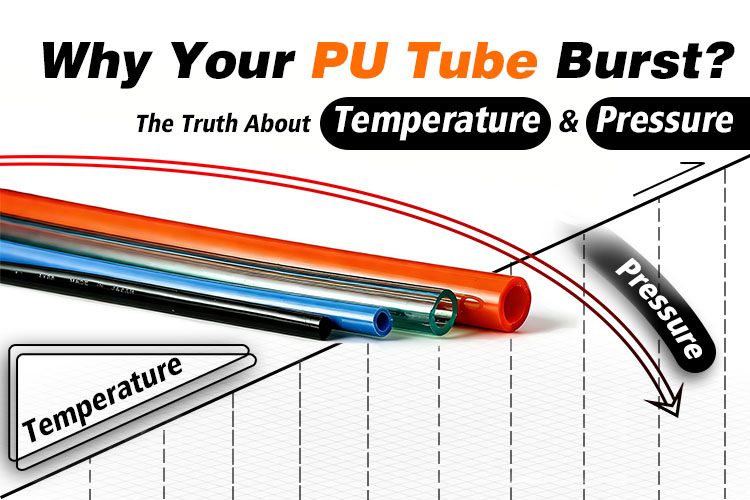
Why a PU Tube Rated for 10 Bar Sometimes Can Only Withstand 5 Bar? Why a PU Tube Rated for 80°C Bursts at 70°C?
Behind these phenomena lies a crucial rule often overlooked by many: the relationship between the temperature of a PU tube and its pressure resistance.
So what effect will increasing temperature have on pressure?
Let's state the conclusion first. As the temperature rises, the pressure resistance of a PU tube decreases sharply. As the temperature drops, its short-term pressure resistance may be maintained or even slightly improved, but at the cost of lost flexibility and the material becoming brittle.
So, why does temperature have such a significant impact on the pressure resistance of PU tubes? How substantial is this effect? And how do you select the appropriate PU tube based on the operating temperature?
Polyurethane is a polymer. Its mechanical strength (such as tensile and burst strength) relies on strong interaction forces between its molecular chains.
When the ambient temperature or the temperature of the medium inside increases, the thermal motion of the polymer molecular chains intensifies, weakening the forces between them. This causes the material to change from tough to softer, with increased elasticity, but the macroscopic manifestation is a significant decrease in the material's mechanical strength. A softer tube wall naturally finds it harder to resist the expansion force of internal pressure.
This "softening" effect not only affects the tube body itself but also impacts the connection between the tube and the fitting. At high temperatures, the softened tube wall may not be held securely by the fitting, making it prone to detachment under pressure.
Furthermore, in a closed fluid system, a temperature increase can cause the medium to expand in volume, potentially generating additional pressure far exceeding the system's normal operating pressure. If the already reduced pressure resistance of the PU tube at this temperature is not considered, the risk of bursting multiplies.
The impact of temperature increase on any hose system is significant, yet it is often overlooked in data sheets. Because most hoses are labeled and advertised with their maximum working pressure and maximum working temperature, a misunderstanding exists: that the hose can simultaneously withstand both its maximum pressure and its maximum temperature.
Generally, the working pressure for fluid connectors and hoses is tested and set at a room temperature of 20°C. If the temperature exceeds 20°C, the working pressure of the hose decreases. This effect is usually non-linear and varies for different brands and formulations of PU tubes (e.g., polyester-based, polyether-based). However, the general trend follows the PU tube temperature-pressure curve shown below:
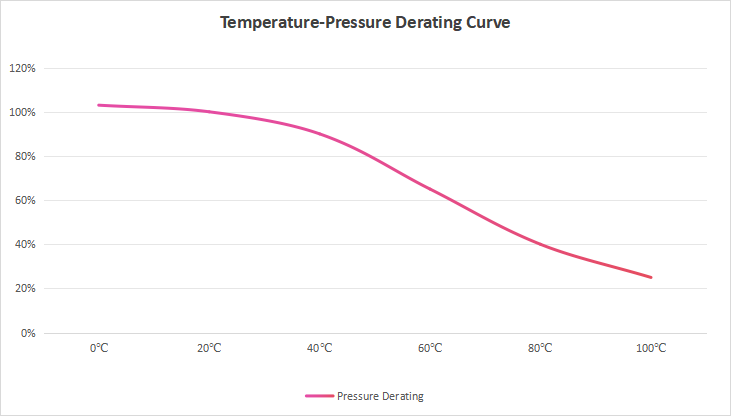
The typical temperature resistance range for conventional PU tubes is approximately -20°C to 80°C. Between 80-100°C, irreversible stickiness and aging occur. Exceeding 100°C can lead to molecular chain breakdown, rendering the tube unusable, and may even cause melting and degradation. Depending on the specific PU material and hardness, the temperature resistance might be slightly higher or lower.
When the temperature falls below 0°C, although the pressure resistance of the PU tube might remain unchanged or increase slightly, the tube becomes hard and brittle. At this point, any impact could cause the PU tube to crack. When the temperature exceeds 80°C, the PU tube undergoes accelerated aging, may even slowly degrade, and its pressure resistance drops significantly.
Therefore, temperature is a critical factor when selecting a PU tube. It determines the fundamental properties (strength, hardness, elasticity) of the PU tube material. Consequently, it directly dictates the maximum safe pressure that the PU tube can withstand in a specific environment.
When selecting a PU tube, you should compare the system's working pressure and peak pressure against the tube's temperature-pressure derating curve, while also allowing for a certain safety margin. This helps avoid failures and risks caused by improper selection.
(FK9009)
 Action Delay of 2-Way Solenoid Valve in Long-Pipe Installation
Action Delay of 2-Way Solenoid Valve in Long-Pipe Installation
 Pilot Orifice Blockage: Hidden Risk in Micro Passages of Solenoid Valve
Pilot Orifice Blockage: Hidden Risk in Micro Passages of Solenoid Valve
 Pneumatic Vacuum Filter: Design Differences between SMC Type and Common Filters
Pneumatic Vacuum Filter: Design Differences between SMC Type and Common Filters
 Why Your PU Tube Burst? The Truth About Temperature & Pressure
Why Your PU Tube Burst? The Truth About Temperature & Pressure
 Temperature Difference: Influence of Condensation on Solenoid Valve Reliability
Temperature Difference: Influence of Condensation on Solenoid Valve Reliability
You May Interest In



Dec 02, 2025 Blog
What are the parts of a pneumatic cylinder?












Apr 18, 2025 Blog
What is an Angle Seat Valve?Links: www.fescolo.com(Pneumatic)
FOKCA ©1998-2025 All Rights Reserved Sitemap