Nov 06, 2025
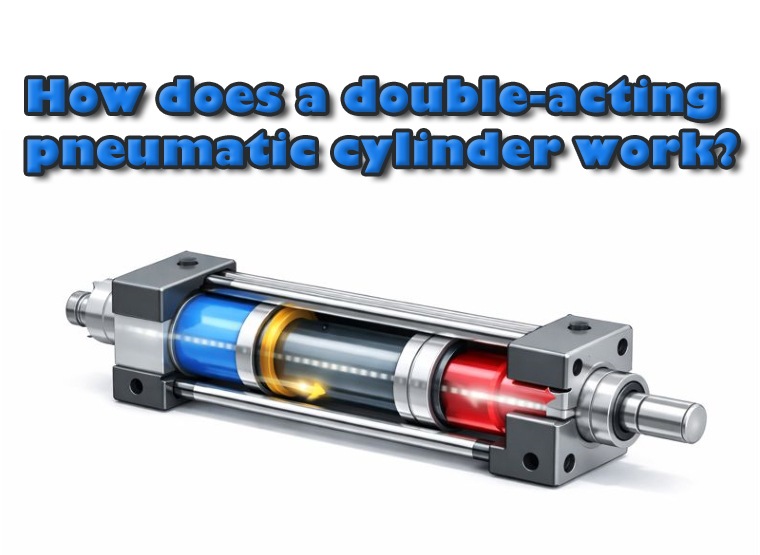
Double-acting pneumatic cylinders are among the most versatile actuators in industrial automation, offering controlled motion in both directions. Unlike single-acting cylinders that rely on a spring for return, double-acting cylinders use air pressure to drive the piston both outward and inward, providing precise force, speed, and position control under a variety of load conditions. Understanding their working principles is essential for engineers designing automated machinery.
A double-acting cylinder consists of a cylindrical body, a piston with a rod, two ports for compressed air, and seals to maintain pressure. Compressed air introduced into one port pushes the piston in the desired direction while the air in the opposite chamber is vented. Reversing the airflow direction reverses piston motion.
The key advantage of this design is bidirectional actuation. Force output is determined by air pressure and piston area, with the piston rod side slightly reducing the effective area in the rod chamber. This asymmetry should be considered in high-precision applications where forward and return forces need to be balanced.
Engineers must account for the following when analyzing double-acting cylinders:
Bore and Rod Diameter:
Larger bores generate higher forces but increase air consumption.
Rod diameter affects stiffness and lateral stability, particularly under side loads.
Stroke Length:
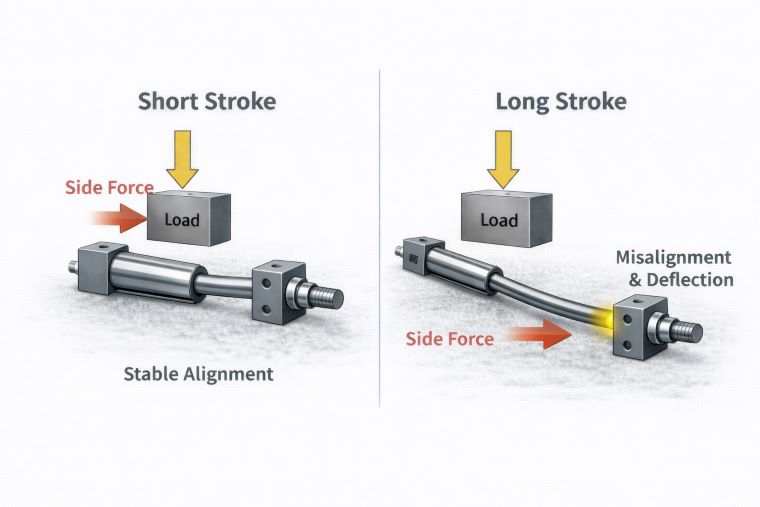
Longer strokes increase the risk of piston rod bending and alignment issues.
For high-speed applications, longer strokes also increase air volume requirements, potentially reducing responsiveness.
Dynamic Load Effects:
Sudden acceleration or deceleration amplifies inertial forces, which can affect cylinder speed, control stability, and component wear.
For high-frequency cycles, consider reinforced end caps and low-friction seals to maintain reliability.
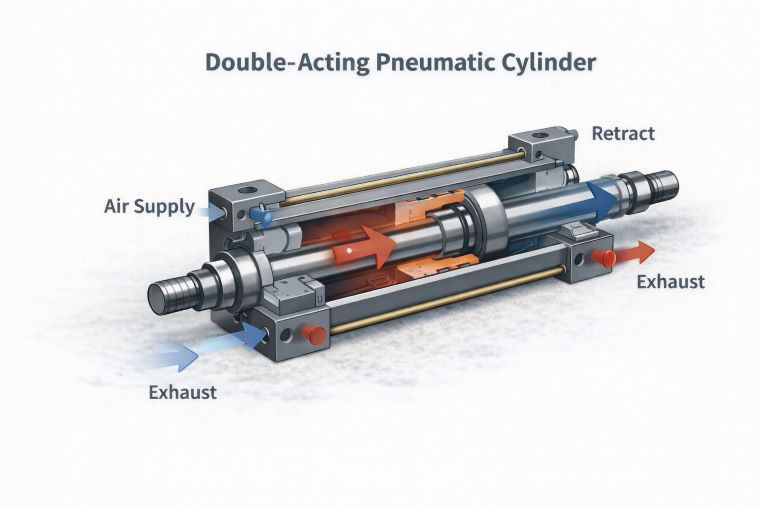
Double-acting cylinders do not operate in isolation; their performance is tightly linked to valve selection, air supply, and system layout.
Direction Control Valves: 4-way, 2-position valves are common, providing reliable switching between extend and retract cycles.
Flow Control: Adjustable throttle valves can regulate speed without affecting force, crucial for precision positioning.
Sensors and Feedback: Magnetic pistons combined with proximity sensors enable repeatable positioning, essential for automation systems with multiple synchronized axes.

Proper sizing and matching between cylinder bore, stroke, and control valves is critical. Oversized cylinders increase air consumption and reduce control accuracy, while undersized cylinders may fail to deliver the required force.
Cylinder mounting affects both precision and service life:
Fixed Mounts (flange, foot, or tie rod) are preferred for high-force applications to minimize lateral deflection.
Rod End Loads must be aligned with the piston axis to prevent uneven seal wear or bending.
Guides or External Supports may be necessary for long strokes or side-loaded applications, ensuring stable motion without compromising speed or force.
Neglecting mounting considerations is a common source of early failure in industrial installations.
Double-acting cylinders are widely used where bidirectional force is required:
Material Handling: Lifting, pushing, or positioning parts on assembly lines.
Packaging Machinery: Accurate, repeatable linear motion for sealing, cutting, or filling operations.
Heavy-Duty Equipment: Moving doors, clamps, or tailgates, where consistent retract and extend forces are critical.
In each case, the cylinder’s bore, stroke, rod size, and mounting must be selected based on both load characteristics and control requirements. Failure to do so can result in reduced cycle life, inconsistent motion, or system inefficiency.
The lifespan of double-acting cylinders is influenced by:
Seal Quality: High-quality seals reduce air leakage and friction, preserving force consistency.
Air Quality: Contaminated or poorly lubricated air accelerates wear.
Operating Conditions: Extreme temperatures, vibration, or misalignment shorten service life.
Scheduled maintenance should include inspection of seals, rods, and mounting, as well as system air quality checks. When used properly, double-acting cylinders can achieve millions of cycles with minimal downtime.
Understanding double-acting pneumatic cylinders goes beyond the basic extend/retract principle:
Load and control characteristics must be evaluated together, not in isolation.
Stroke length, bore, and rod diameter directly impact force, speed, and alignment stability.
Valve selection and airflow control are as important as the cylinder itself.
Mounting and mechanical integration determine motion precision and service life.
Maintenance and air quality ensure consistent, long-term operation.
By integrating these factors into design and selection, engineers can optimize double-acting cylinders for performance, reliability, and efficiency in automated systems.
(FK9027)
 Mini Type Pneumatic Push In Fittings: Flow Difference Between Straight and Elbow Designs
Mini Type Pneumatic Push In Fittings: Flow Difference Between Straight and Elbow Designs
 Influence of Exhaust Throttling of 3-Way Solenoid Valve on Actuator Return Speed
Influence of Exhaust Throttling of 3-Way Solenoid Valve on Actuator Return Speed
 Influence of Coil Overheating on Continuous Duty of 2-Way Solenoid Valve
Influence of Coil Overheating on Continuous Duty of 2-Way Solenoid Valve
 PVC Flexible Tubing vs PU Tubing: Cost Difference Analysis in Equipment Internal Routing
PVC Flexible Tubing vs PU Tubing: Cost Difference Analysis in Equipment Internal Routing
 The principle and characteristics of vacuum generators
The principle and characteristics of vacuum generators
You May Interest In
Links: www.fescolo.com(Pneumatic)
FOKCA ©1998-2025 All Rights Reserved Sitemap