Nov 07, 2025
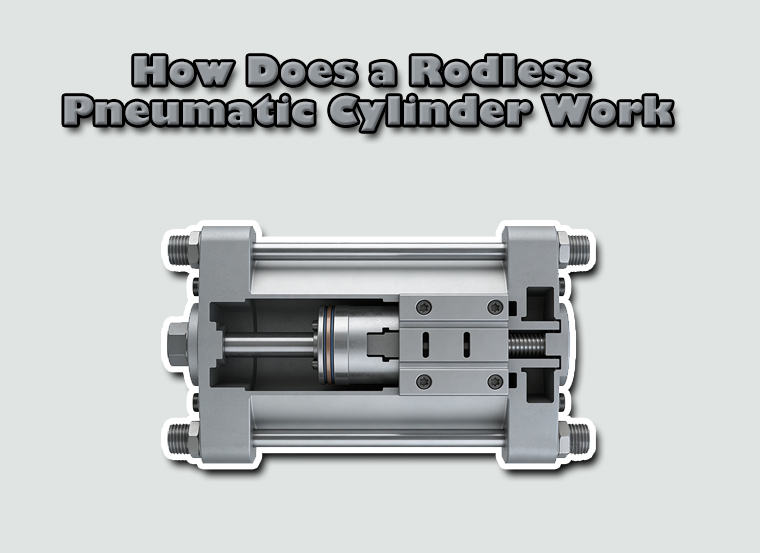
Rodless pneumatic cylinders are designed to solve a specific mechanical problem: how to generate long, stable linear motion when installation space does not allow a traditional piston rod to extend. Instead of transmitting force through an exposed rod, a rodless cylinder transfers motion internally to an external carriage, allowing the load to move along the cylinder body itself. This structural difference fundamentally changes how force, sealing, guidance, and load handling must be engineered.
Understanding how a rodless pneumatic cylinder works requires looking beyond basic airflow and focusing on force transmission, sealing mechanisms, and load guidance, which distinguish it from standard rod-type pneumatic cylinders.
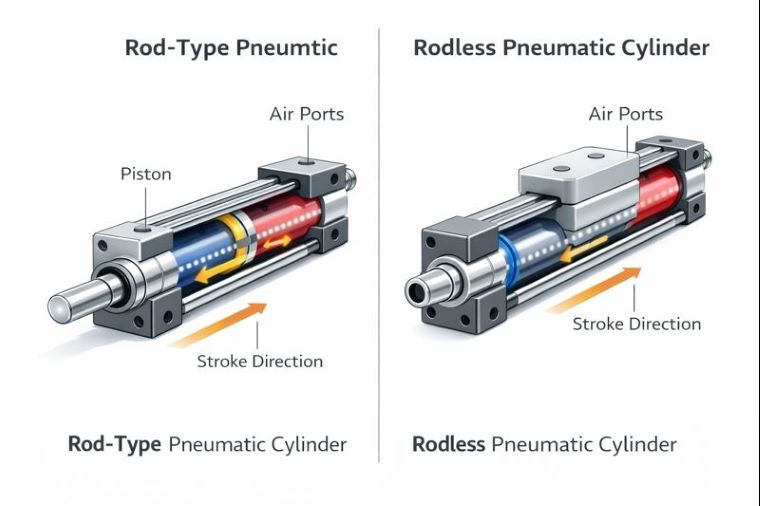
At the core of a rodless pneumatic cylinder is a piston moving inside a sealed cylinder bore, just like a conventional air cylinder. Compressed air alternately enters either side of the piston through two ports, driving it forward and backward. The difference lies in how this internal piston motion is transferred outside the cylinder.
Instead of a piston rod penetrating the end cap, the piston is mechanically or magnetically coupled to an external carriage that runs along the length of the cylinder body. As the piston moves internally, the carriage follows in the same direction, producing usable linear motion without any increase in overall cylinder length.
This configuration allows stroke lengths that can be several times longer than the cylinder body itself, making rodless pneumatic cylinders particularly suitable for long-travel automation systems.
Rodless pneumatic cylinders typically use one of two coupling methods to transmit motion.
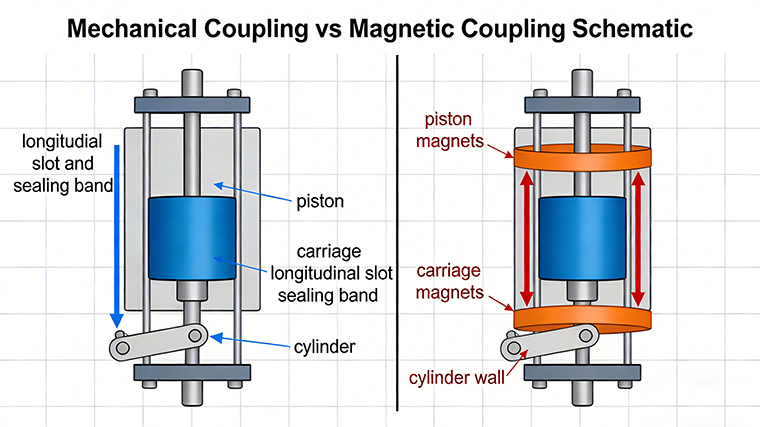
In mechanically coupled rodless pneumatic cylinders, a longitudinal slot runs along the cylinder tube. The internal piston is physically connected to the external carriage through this slot. A flexible sealing band continuously closes the slot, preventing air leakage while allowing movement. This design provides rigid force transmission and higher load capacity, making it suitable for applications where external forces or moments are present.
In magnetically coupled rodless pneumatic cylinders, there is no physical opening in the cylinder body. Strong permanent magnets embedded in the piston couple with magnets in the external carriage through the cylinder wall. While this design eliminates the sealing slot and reduces leakage risk, the maximum transferable force is limited. Excessive loads or sudden impacts can cause magnetic decoupling between the piston and carriage.
Sealing plays a more critical role in rodless pneumatic cylinders than in rod-type designs. In mechanically coupled designs, the longitudinal slot must remain sealed under pressure while allowing continuous movement. This is achieved through metal or polymer sealing strips combined with internal cylinder seals.
Wear, contamination, or misalignment in these sealing components can lead to air leakage, reduced efficiency, and unstable motion. As a result, rodless pneumatic cylinders are generally more sensitive to air quality and installation accuracy than standard pneumatic cylinders.
Magnetically coupled designs simplify sealing but rely entirely on magnetic force integrity, which places stricter limits on allowable loads.
Unlike rod-type air cylinders that often rely on external guides, rodless pneumatic cylinders frequently integrate guidance directly into the carriage assembly. Linear bearings or guide rails are built into the cylinder body to support loads and resist bending moments caused by off-center forces.
This integrated guidance allows the cylinder to function as both an actuator and a linear guide, reducing system complexity. However, it also means that load orientation, center of gravity, and applied moments must be evaluated carefully during selection. Improper load distribution can significantly shorten service life.
Rodless pneumatic cylinders are commonly used in applications requiring smooth, continuous motion over long distances. Motion speed is controlled by airflow regulation through pneumatic solenoid valves, while end-position cushioning reduces impact forces at stroke limits.
Due to their long stroke lengths and larger moving masses, rodless pneumatic cylinders exhibit different dynamic behavior compared to compact rod-type pneumatic cylinders. Improper exhaust capacity or flow control can result in vibration, carriage oscillation, or inconsistent positioning.
Rodless pneumatic cylinders are widely used in automation systems where long stroke, compact layout, and clean linear motion are required. Typical applications include:
Transfer units in packaging and assembly lines
Pick-and-place systems with extended horizontal travel
Conveyor diverters and positioning stations
Automated storage and retrieval equipment
In these systems, minimizing machine footprint while maintaining long travel distance is often the primary design driver.
Selecting a rodless pneumatic cylinder is not a direct replacement decision for a rod-type air cylinder. Stroke length, load mass, applied moments, coupling method, air quality, and mounting accuracy must be evaluated together at the system level.
When properly selected and installed, rodless pneumatic cylinders provide efficient, space-saving linear motion. When misapplied, they are more likely to suffer from sealing wear, leakage, or coupling failure.
Understanding how a rodless pneumatic cylinder works is therefore essential not only for correct operation, but for long-term reliability in automated equipment.
(FK9027)
 Mini Type Pneumatic Push In Fittings: Flow Difference Between Straight and Elbow Designs
Mini Type Pneumatic Push In Fittings: Flow Difference Between Straight and Elbow Designs
 Influence of Exhaust Throttling of 3-Way Solenoid Valve on Actuator Return Speed
Influence of Exhaust Throttling of 3-Way Solenoid Valve on Actuator Return Speed
 Influence of Coil Overheating on Continuous Duty of 2-Way Solenoid Valve
Influence of Coil Overheating on Continuous Duty of 2-Way Solenoid Valve
 PVC Flexible Tubing vs PU Tubing: Cost Difference Analysis in Equipment Internal Routing
PVC Flexible Tubing vs PU Tubing: Cost Difference Analysis in Equipment Internal Routing
 The principle and characteristics of vacuum generators
The principle and characteristics of vacuum generators
You May Interest In

Nov 21, 2025 Blog
How does a pneumatic air cylinder work?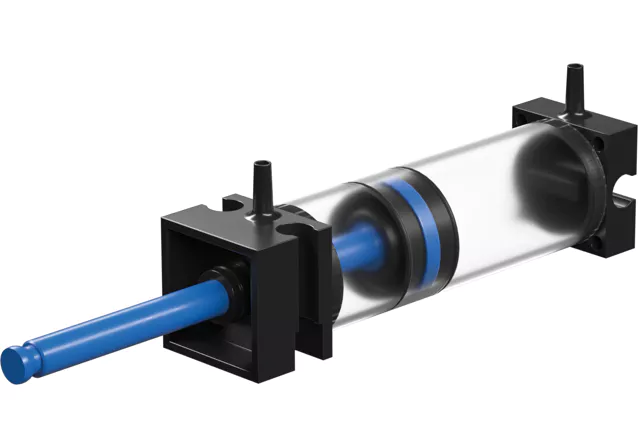
Nov 20, 2025 Blog
How mush air does a pneumatic cylinder use?
Nov 15, 2025 Blog
How long do pneumatic cylinders last?
Nov 14, 2025 Blog
How fast can a pneumatic cylinder move?
Nov 12, 2025 Blog
What is a single acting cylinder?

Links: www.fescolo.com(Pneumatic)
FOKCA ©1998-2025 All Rights Reserved Sitemap