Jan 20, 2026
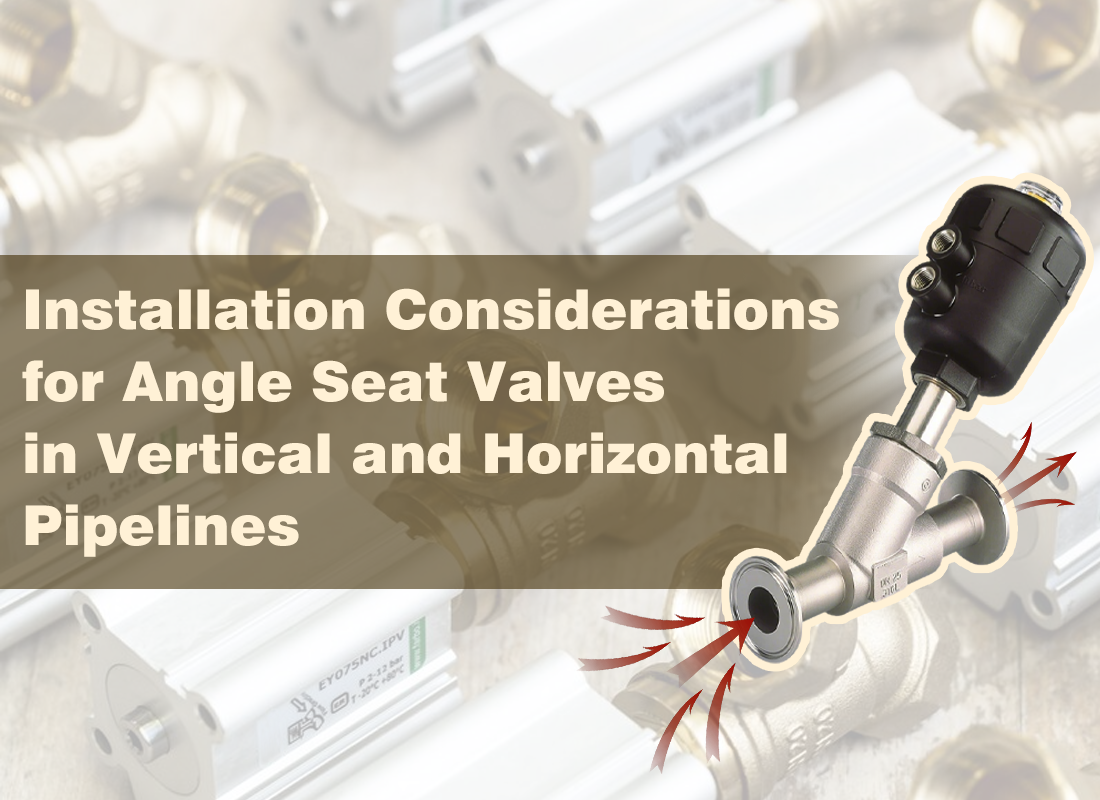
Angle seat valves are widely used in industrial automation due to their high flow capacity, low pressure drop, and fast switching performance. However, in real-world installations, valve failures are often linked not to product quality but to improper installation orientation. In vertical and horizontal pipelines, gravity, condensate behavior, and actuator positioning play a critical role in long-term reliability.
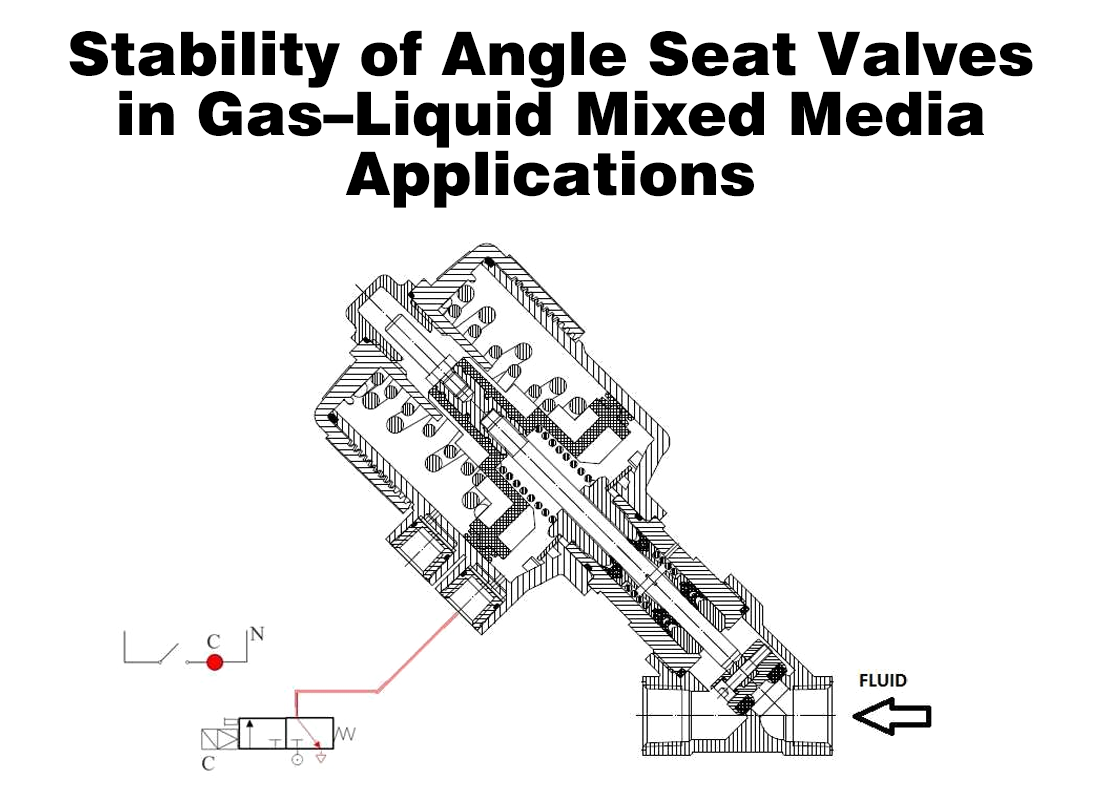
An angle seat valve relies on axial movement of the valve stem and plug. The gravity effect acting on these components changes depending on whether the valve is installed in a vertical or horizontal pipeline. If this factor is ignored, sealing wear and unstable operation may occur over time, especially in continuous-duty systems.
Understanding these mechanical influences helps engineers avoid hidden risks during installation, particularly in compact or space-limited equipment layouts.
In vertical pipeline installations, media may flow upward or downward. When flow direction aligns with the valve opening movement, the valve operates more smoothly with reduced mechanical stress. This is common in steam and hot water systems.
When flow is downward, gravity adds to the closing force, which can affect sealing behavior. In such cases, actuator orientation becomes critical. Keeping the pneumatic actuator facing upward or sideways reduces internal wear and prevents moisture from accumulating inside the actuator housing.
In horizontal pipelines, condensate tends to settle at the bottom of the pipe. Over time, this condensate accumulation can remain inside the valve body, accelerating corrosion and seal degradation.
Slightly tilting the valve or ensuring proper drainage upstream helps reduce liquid retention. This small adjustment often makes a significant difference in valve lifespan, particularly in steam and compressed air systems.
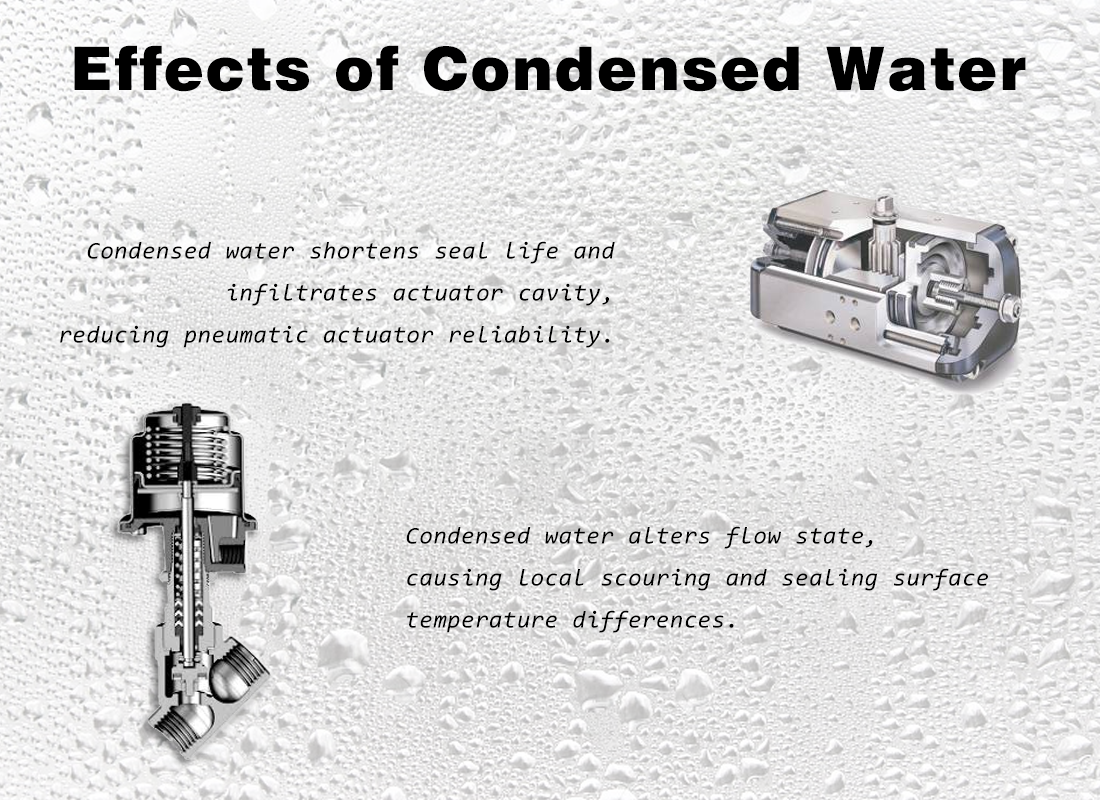
Condensate changes internal flow conditions and introduces temperature gradients across sealing surfaces. Over time, this affects both the valve seat and the actuator. Moisture entering the actuator reduces pneumatic actuator reliability, leading to slower response or incomplete switching.
Designing the installation to encourage natural drainage is one of the most effective preventive measures.
The mounting direction of the actuator directly affects internal seals, springs, and pistons. Downward-facing actuators are more vulnerable to moisture ingress, especially in outdoor or high-humidity environments.
Correct actuator positioning not only improves reliability but also simplifies future maintenance, an important consideration for equipment engineers and end users alike.
| Installation Orientation | Key Risk Factors | Recommended Practice |
|---|---|---|
| Vertical, flow up | Gravity-assisted closing | Actuator up or horizontal |
| Vertical, flow down | Combined gravity and pressure | Avoid actuator facing down |
| Horizontal pipeline | Condensate accumulation | Slight tilt or drainage design |
| Steam service | Thermal cycling, condensate | Install with drainage priority |
Selecting the right valve is only part of the solution. Proper installation orientation of angle seat valves ensures stable operation, longer service life, and lower maintenance costs. For distributors and system integrators, sharing these installation insights adds tangible value beyond product supply.
By considering gravity, condensate behavior, and actuator orientation together, engineers can significantly reduce avoidable valve failures in both vertical and horizontal pipeline systems.
(FK9025)
 Why Quick Exhaust Valves Are Needed in Pneumatic Systems
Why Quick Exhaust Valves Are Needed in Pneumatic Systems
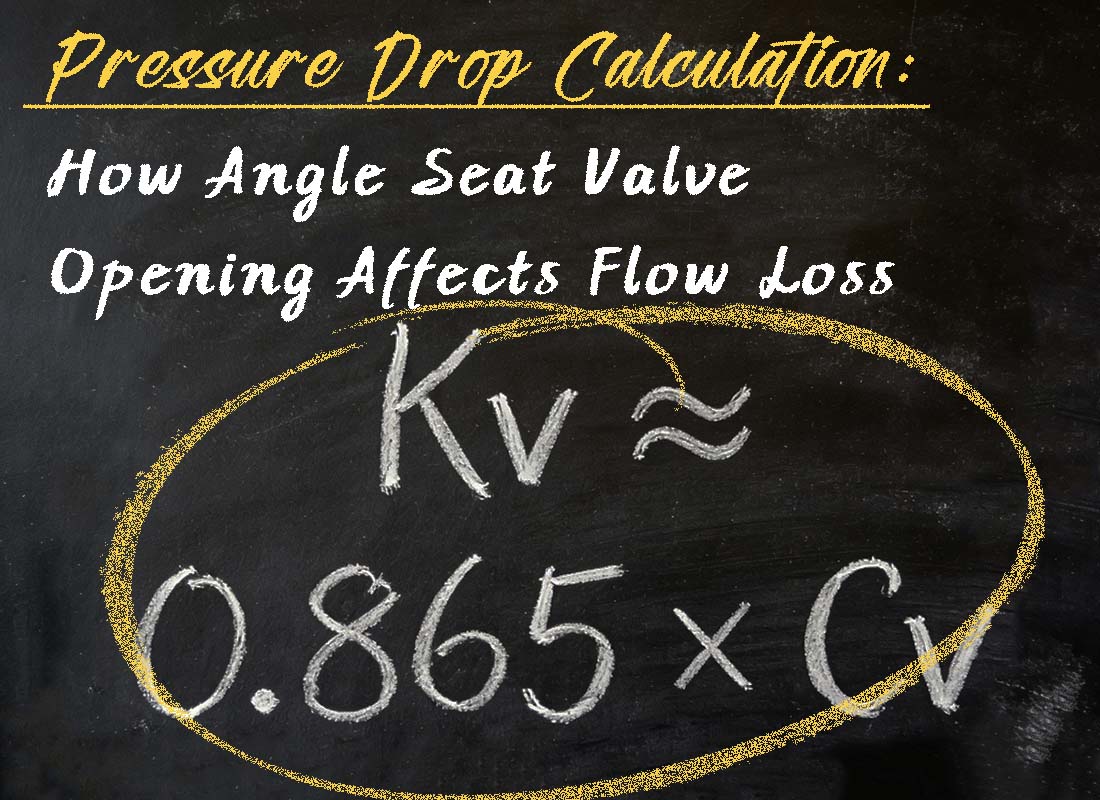 Pressure Drop Calculation: How Angle Seat Valve Opening Affects Flow Loss
Pressure Drop Calculation: How Angle Seat Valve Opening Affects Flow Loss
 IP Protection Rating of Solenoid Valve Coils
IP Protection Rating of Solenoid Valve Coils
 Can PP Polypropylene Tube Replace Certain Metal Piping in Low-Pressure Systems
Can PP Polypropylene Tube Replace Certain Metal Piping in Low-Pressure Systems
 UV Resistant Polyurethane Tubing vs PVC Tubing for Outdoor Applications
UV Resistant Polyurethane Tubing vs PVC Tubing for Outdoor Applications
You May Interest In

Dec 12, 2025 Blog
What Is a Globe Control Valve?

Dec 11, 2025 Blog
Two ways for a globe valve to be bidirectional
Dec 10, 2025 Blog
How Does a Manual Globe Control Valve Work?

Dec 09, 2025 Blog
Working Principle of Check Valves

Dec 08, 2025 Blog
Can a Globe Valve Be Used to Control Steam Pressure
Dec 08, 2025 Blog
How Does a Globe Valve Work
Dec 04, 2025 Blog
How to Identify Gate Valve and Globe Valve

Dec 06, 2025 Blog
How to check pneumatic solenoid valve?

Dec 04, 2025 Blog
How does a single solenoid valve work?
Dec 03, 2025 Blog
What is double acting solenoid valve?
Dec 02, 2025 Blog
How to clean a pneumatic solenoid valve?
Dec 01, 2025 Blog
How to Wire and Install a Pneumatic Solenoid Valve?
Nov 30, 2025 Blog
How to select pneumatic solenoid valve?
Nov 29, 2025 Blog
Operational Mechanism of Pneumatic Solenoid Valves

Nov 27, 2025 Blog
What is pilot operated solenoid valve?Links: www.fescolo.com(Pneumatic)
FOKCA ©1998-2025 All Rights Reserved Sitemap