Dec 11, 2025
Understanding the distinction between male and female fittings is crucial for anyone working with plumbing, hydraulics, or any fluid transfer systems.
Accurate identification of male and female fittings prevents costly mistakes and ensures secure, leak-free connections. We’ll delve into the practical aspects of these fittings, covering their common uses and the importance of selecting the correct type for specific applications. Whether you’re a DIY enthusiast or a seasoned professional, this guide will provide valuable insights into the world of fittings.
Male Fitting is a type of pipe fitting characterized by external threads on the outside of the connector. It is typically made of brass, stainless steel, carbon steel, or plastic. Structurally, the threads protrude outward and fit tightly with female threads, providing both mechanical stability and a secure seal. Male fittings are widely used for pipe extensions, branching, valve connections, as well as in pneumatic, hydraulic, and water supply or drainage systems, and are especially suitable for piping systems that require quick assembly, disassembly, and maintenance.
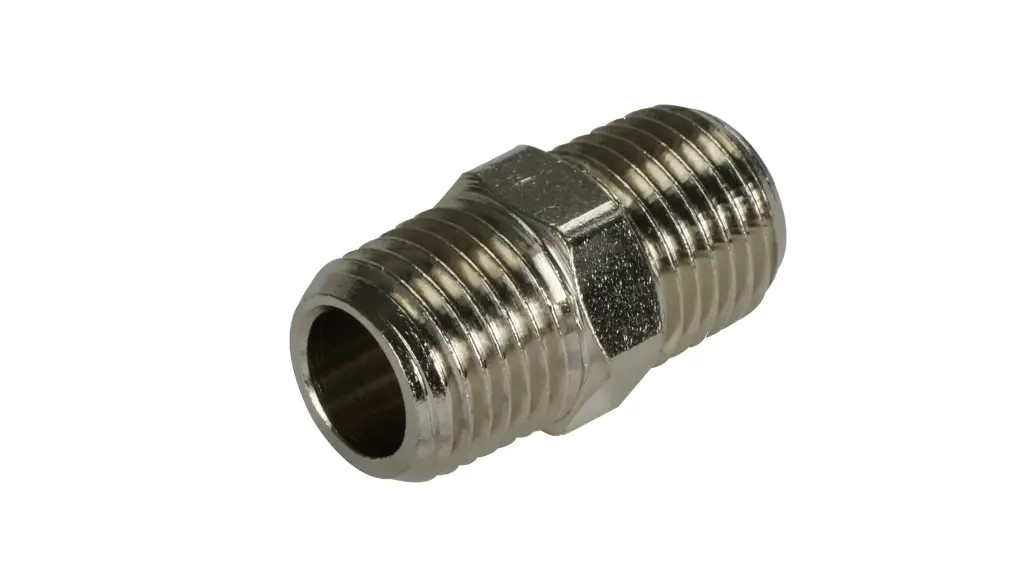

Structural Features: The thread is on the outside of the fitting, protruding, and one end can be directly screwed into a female threaded pipe fitting or connector.
Function:To mate with the female thread, achieving pipe connection, providing mechanical fixation and sealing.
Applications:
Pipe extension, adapter pipe, tee or elbow connection
Valve interface, equipment port access
Quick assembly/disassembly or maintenance scenarios
Female Fitting is a type of pipe fitting characterized by internal threads on the inside of the connector. It is typically made of brass, stainless steel, carbon steel, or plastic. Structurally, the threads are recessed inward to receive male threads, providing both mechanical stability and a secure seal. Female fittings are widely used for pipe interfaces, valve connections, tees, elbows, and in pneumatic, hydraulic, or water supply and drainage systems, and are especially suitable for piping systems that require reliable connections and easy maintenance.
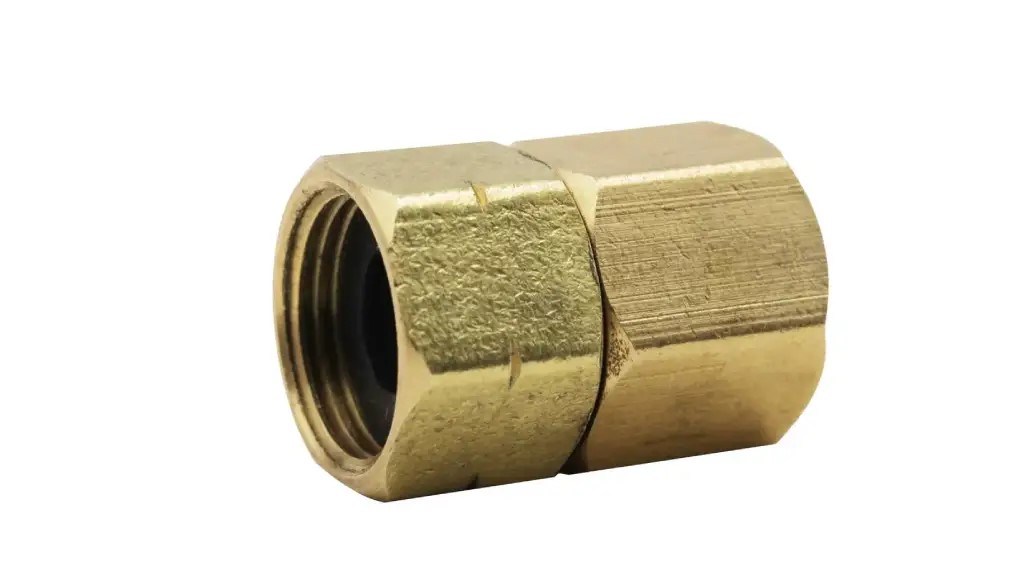

Structural Features:The thread is on the inside of the fitting, concave, allowing the insertion of a male threaded pipe fitting or connector.
Function:After the internal thread is screwed into the external thread of the male fitting, pipe connection and sealing are achieved, and support and stable connection are also provided.
Applications:
Pipe interface, valve interface, tee, elbow, etc.
Combined with male threaded pipe fittings, extending or branching pipelines.
Commonly used in industrial, hydraulic or pneumatic piping.
| Item | Male Fitting | Female Fitting |
|---|---|---|
| Thread Type | External Thread (Threaded Outside) | Internal Thread (Threaded Inside) |
| Structural Features | Threads are on the outside of the fitting, can be directly inserted into a female threaded port | Threads are on the inside of the fitting, can receive a male threaded pipe or fitting |
| Function | Mainly used to be inserted into a female fitting to complete the connection and sealing | Mainly used to receive a male fitting to achieve connection and sealing |
| Application | Pipe ends, extensions, adapters, quick-connect fittings, etc. | Pipe interfaces, valve connections, tees, elbows, etc. |
| Advantages | Easy to insert, quick to install | Compatible with various male threaded fittings, highly adaptable |
| Precautions | Threads are exposed, must ensure leak prevention (use sealing tape or sealant) | Thread depth and size must match male threads to avoid loosening or leakage |
| Difference Summary | Threads are outside, “protruding” | Threads are inside, “recessed” |
Proper Pairing: When connecting, ensure the male thread matches the corresponding female thread size to avoid leaks or damage caused by thread mismatch.
Proper Tightening: As a fitting manufacturer, we receive a lot of feedback from customers about using improper tools and excessive force, leading to thread damage or deformation.
Leak Prevention: Apply PTFE tape or pipe thread sealant to male threads to ensure a reliable seal.
Regular Inspection: In addition to proper use, regularly inspect fittings for leaks, looseness, or thread wear.
Clean Fittings: Exposed threads easily accumulate dust, oil, and impurities; keep the contact surfaces clean.
(9016)
 Why Globe Valve Performs Better in Frequent Opening and Closing Applications
Why Globe Valve Performs Better in Frequent Opening and Closing Applications
 Rubber hose vs Polyurethane tubing vs Nylon tubing: Choosing the Right Pneumatic Hose Material
Rubber hose vs Polyurethane tubing vs Nylon tubing: Choosing the Right Pneumatic Hose Material
 How Does Mesh Affect the Performance of Pneumatic Silencers?
How Does Mesh Affect the Performance of Pneumatic Silencers?
 Hydraulic Quick Couplers: Maintenance Details Most People Overlook
Hydraulic Quick Couplers: Maintenance Details Most People Overlook
 Globe Valve Installation Direction Errors and Corrosion Risks You Can’t Ignore
Globe Valve Installation Direction Errors and Corrosion Risks You Can’t Ignore
You May Interest In



Dec 02, 2025 Blog
What are the parts of a pneumatic cylinder?












Apr 18, 2025 Blog
What is an Angle Seat Valve?Links: www.fescolo.com(Pneumatic)
FOKCA ©1998-2025 All Rights Reserved Sitemap