Jan 06, 2026
Measuring pipes and fittings is crucial. First, it ensures that pipes and fittings are correctly connected to prevent leaks and improve system safety. Second, it reduces installation errors and rework costs, and maintains system performance and lifespan.
Pipes are primarily used to convey fluids such as air, water, oil, or gas. They are usually straight sections with standardized lengths and are responsible for the actual transmission of the fluid. Fittings, on the other hand, are used to connect pipes, change flow direction, create branches, or reduce or expand size. They do not directly transport fluids but assist pipes in forming the overall piping layout. Working together, pipes and fittings form a complete fluid conveyance system—pipes serve as the “flow paths,” while fittings act as the “connection and control nodes.”

Nominal Diameter (DN):
This is a standardized size designation used to identify the bore size of pipes, fittings, valves, and other components. It is usually a rounded integer (e.g., DN50, DN100) and does not represent any actual measured diameter. Its main function is to provide a unified naming system, ensuring that pipes and accessories produced by different manufacturers can be connected and matched with each other.
Outside Diameter (OD):
Refers to the actual diameter of the external cylindrical surface of a pipe or tubing. This is a crucial physical dimension, especially when pipes need to be butted, welded, or installed with clamps. For many standard pipes (such as stainless steel pipes, PVC pipes), the outside diameter is usually a fixed value.
Inside Diameter (ID):
Refers to the actual diameter of the internal flow passage of a pipe. It directly determines the flow area of the fluid and is a key basis for calculating process parameters such as flow rate and velocity. Inside Diameter = Outside Diameter – 2 × Wall Thickness.
Wall Thickness:
Refers to the thickness of the pipe wall. It is directly related to the pressure-bearing capacity, weight, and cost of the pipe. Wall thickness is selected and standardized based on factors such as the pressure the pipe needs to withstand, the strength of the material, and corrosion resistance requirements.
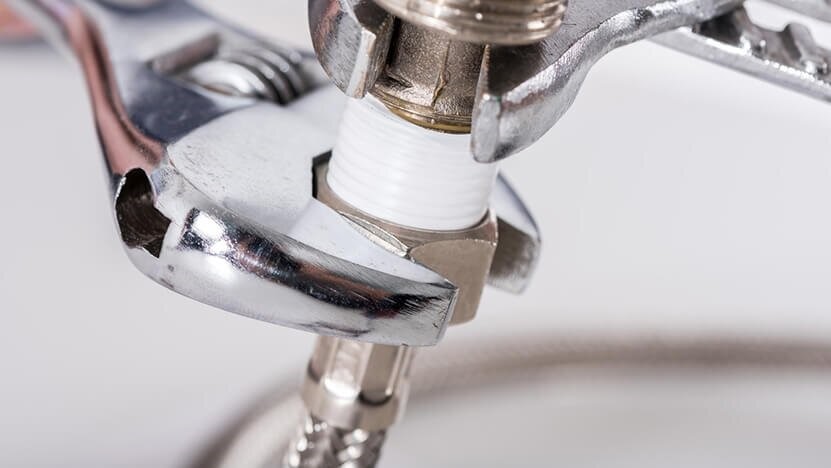
Before installing a PVC piping system, accurate measurement of the pipe length is essential for a proper fit. Begin by using a measuring tape or ruler to measure the distance between two fittings. Make sure to measure from the inside edges or the center of the fittings, rather than the outside edges, to avoid dimensional errors.

After obtaining the initial measurement, add the length of the fittings to the total distance. The fitting length refers to the full distance from one end to the other, including any threaded or socketed sections. To allow for minor adjustments and to prevent cutting mistakes, it is recommended to add an extra 1 to 2 inches to the final measurement.

Once the measurement is confirmed, mark the PVC pipe at the required length and cut it accordingly. After cutting, use sandpaper or a deburring tool to smooth and remove any rough edges. This step ensures that the pipe can be easily inserted into the fittings and creates a snug, reliable connection during installation.

After cutting the pipe, use your sandpaper or deburring tool to smooth out any rough edges. This will ensure a snug fit when you insert the pipe into the fittings.

Accurate measurement of pipes and fittings is key to proper installation, safety, and system performance. Before measuring, it is important to understand basic parameters such as DN, OD, ID, and wall thickness to ensure correct sizing and compatibility.
Measurement involves determining the distance between fittings, adding the fitting lengths, and allowing extra space for adjustments. After marking and cutting the pipe, smoothing the edges ensures easy assembly and a secure, leak-free connection. This process helps reduce errors, save materials, and improve installation efficiency.
(FK9016)
 Impact of Trapped Media in the Valve Cavity on Restart Performance of Pneumatic Ball Valves
Impact of Trapped Media in the Valve Cavity on Restart Performance of Pneumatic Ball Valves
 Wear Path Analysis of Pneumatic Ball Valve Under Frequent Cycling Conditions
Wear Path Analysis of Pneumatic Ball Valve Under Frequent Cycling Conditions
 Mini Push In Fittings: Aging Problems of Plastic Bodies in Humid Environments
Mini Push In Fittings: Aging Problems of Plastic Bodies in Humid Environments
 Mini Type Pneumatic Push In Fittings: Flow Difference Between Straight and Elbow Designs
Mini Type Pneumatic Push In Fittings: Flow Difference Between Straight and Elbow Designs
 Influence of Exhaust Throttling of 3-Way Solenoid Valve on Actuator Return Speed
Influence of Exhaust Throttling of 3-Way Solenoid Valve on Actuator Return Speed
You May Interest In



Dec 02, 2025 Blog
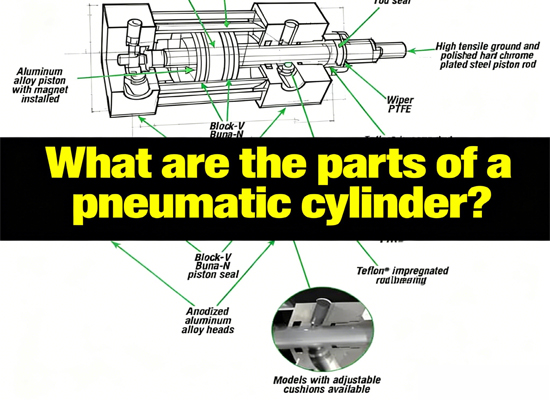
What are the parts of a pneumatic cylinder?












Apr 18, 2025 Blog
What is an Angle Seat Valve?Links: www.fescolo.com(Pneumatic)
FOKCA ©1998-2025 All Rights Reserved Sitemap