Nov 19, 2025
NPT stands for National Pipe Taper, known in Chinese as the "American National Tapered Pipe Thread." The threads of this type of fitting are tapered, resembling a pin, with the diameter gradually increasing from one end to the other. It creates a seal through the taper of the threads and requires the use of Teflon tape or pipe thread sealant to achieve an effective seal. This NPT fitting is widely used in various fluid (water, gas, oil) pipeline systems across North America.
Tapered thread refers to a tapered thread, the core characteristic of which is that the thread diameter gradually decreases along its length.
In NPT (Non-Pipeline Technology), the taper ratio is: 1 inch of diameter reduction per 16 inches of thread length. That is, the diameter decreases by 1/16 inch per inch of thread length. This structure allows the thread to create a wedge-like effect when tightened, forming a seal through the interference fit between the metal parts.
Excellent Sealing Performance:The tapered design ensures a tight metal-to-metal contact when tightened, making the self-sealing capability of NPT fittings its biggest advantage.
High Pressure Resistance:Due to the clamping force created at the connection point by its tapered structure, NPT fittings can withstand medium to high pressure conditions.
Low Cost:NPT fittings have a very simple structure, without additional seals or complex mechanical mechanisms, which reduces the requirements for manufacturing capabilities.
Wide Range of Sizes and Materials
NPT pipe fittings can be manufactured from a variety of materials to meet different environmental needs
Brass: Commonly used in pneumatic, hydraulic, and low-pressure systems
Stainless Steel: Suitable for corrosive environments, sanitary industries, and high-pressure conditions
Carbon Steel: The first choice for industrial hydraulic systems, with strong pressure resistance
Plastic (PVC/CPVC): Chemical and low-pressure water treatment systems
Bronze, Copper, etc.: Specific applications such as marine and HVAC.
| Characteristic | NPT | NPS / Straight Threads (BSPP, G-Thread, etc.) |
|---|---|---|
| Thread Shape | Tapered | Straight / Cylindrical |
| Sealing Method | Seals on the threads themselves (often enhanced with PTFE tape or thread sealant) | Does not self-seal; requires O-rings, gaskets, or metal-to-metal sealing surfaces |
| Pressure Capability | Suitable for medium to high-pressure systems | Better suited for low-pressure or applications requiring frequent disassembly |
| Tightening Behavior | Tightens progressively due to wedging and interference fit | Tightening to the end does not create a seal |
| Need for Sealant | Typically required | Usually not required (sealed by O-ring or gasket) |
Measuring NPT fittings primarily involves determining their nominal diameter rather than directly measuring the physical diameter of the threads. Here are the simple measurement steps:
Measure the outer diameter: For male threads, use calipers to measure the major diameter of the threads.
Refer to a size chart: Compare the measured outer diameter with a standard NPT size reference chart to identify the corresponding nominal diameter.
A quick estimation reference:
The major diameter of a 1/8-inch NPT male thread is approximately 10.3 mm.
The major diameter of a 1/4-inch NPT male thread is approximately 13.7 mm.
The major diameter of a 1/2-inch NPT male thread is approximately 21.0 mm.
(9016)
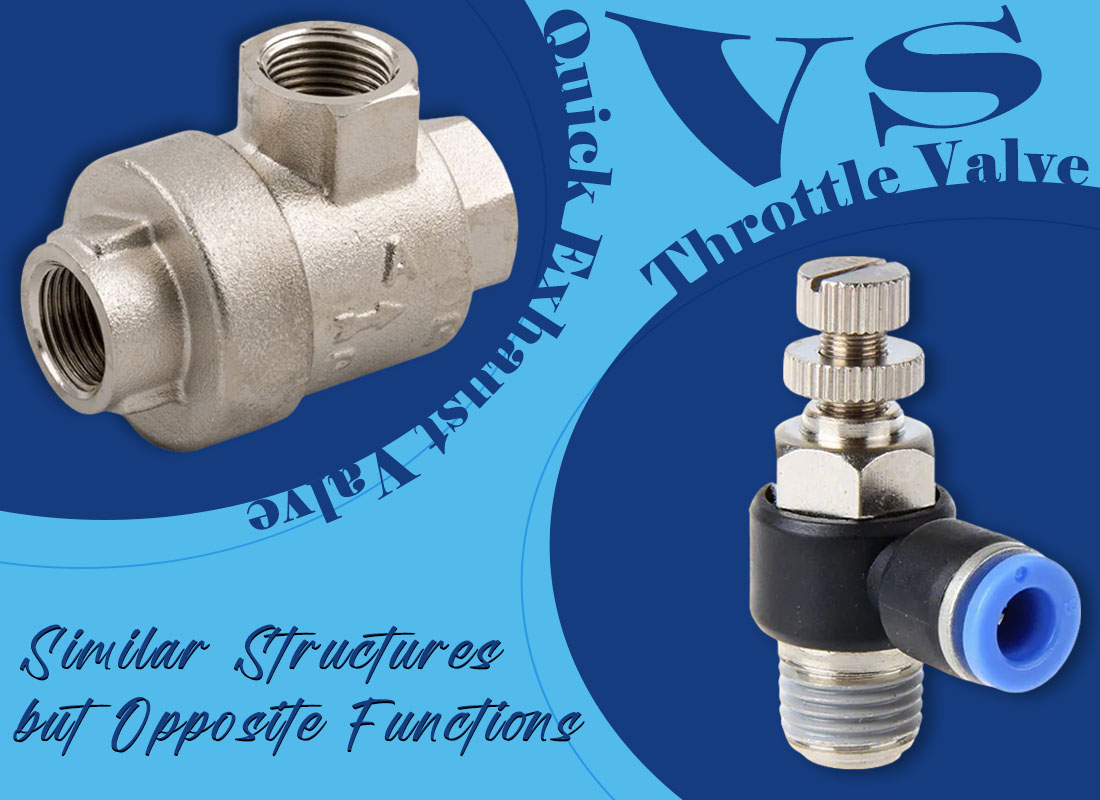 Quick Exhaust Valve vs Throttle Valve: Similar Structures but Opposite Functions
Quick Exhaust Valve vs Throttle Valve: Similar Structures but Opposite Functions
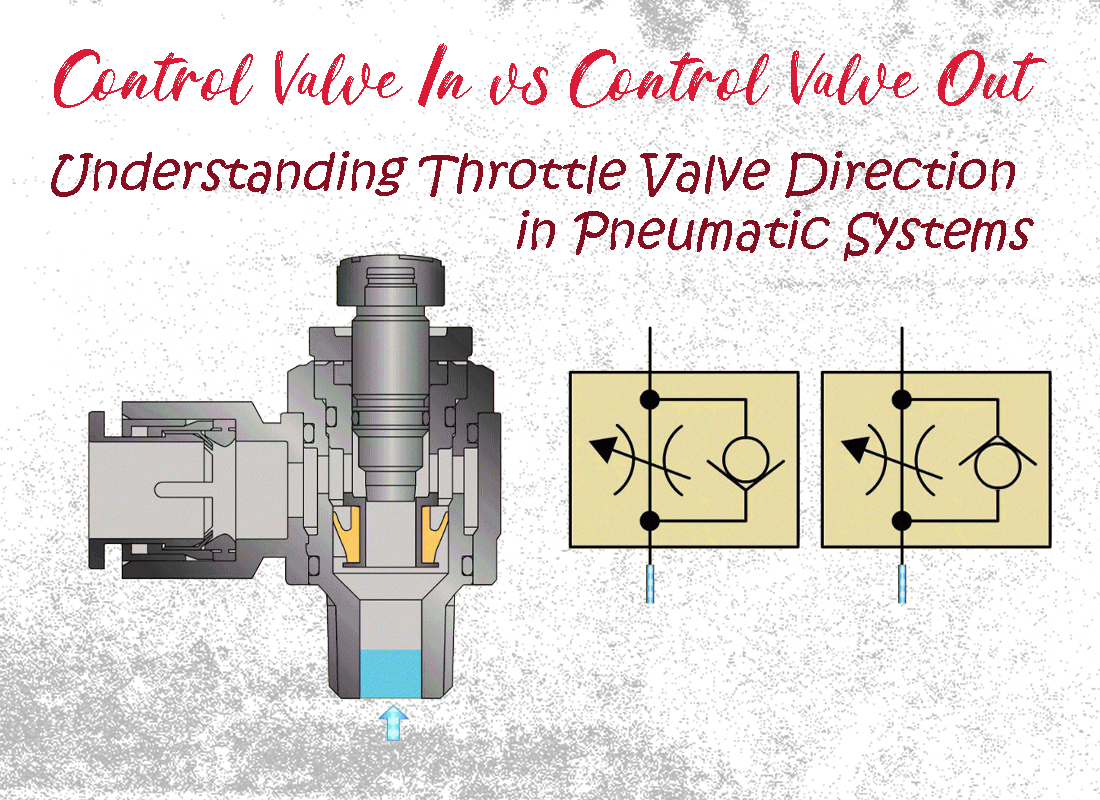 Control Valve In vs Control Valve Out: Understanding Throttle Valve Direction in Pneumatic Systems
Control Valve In vs Control Valve Out: Understanding Throttle Valve Direction in Pneumatic Systems
 Why Quick Exhaust Valves Are Needed in Pneumatic Systems
Why Quick Exhaust Valves Are Needed in Pneumatic Systems
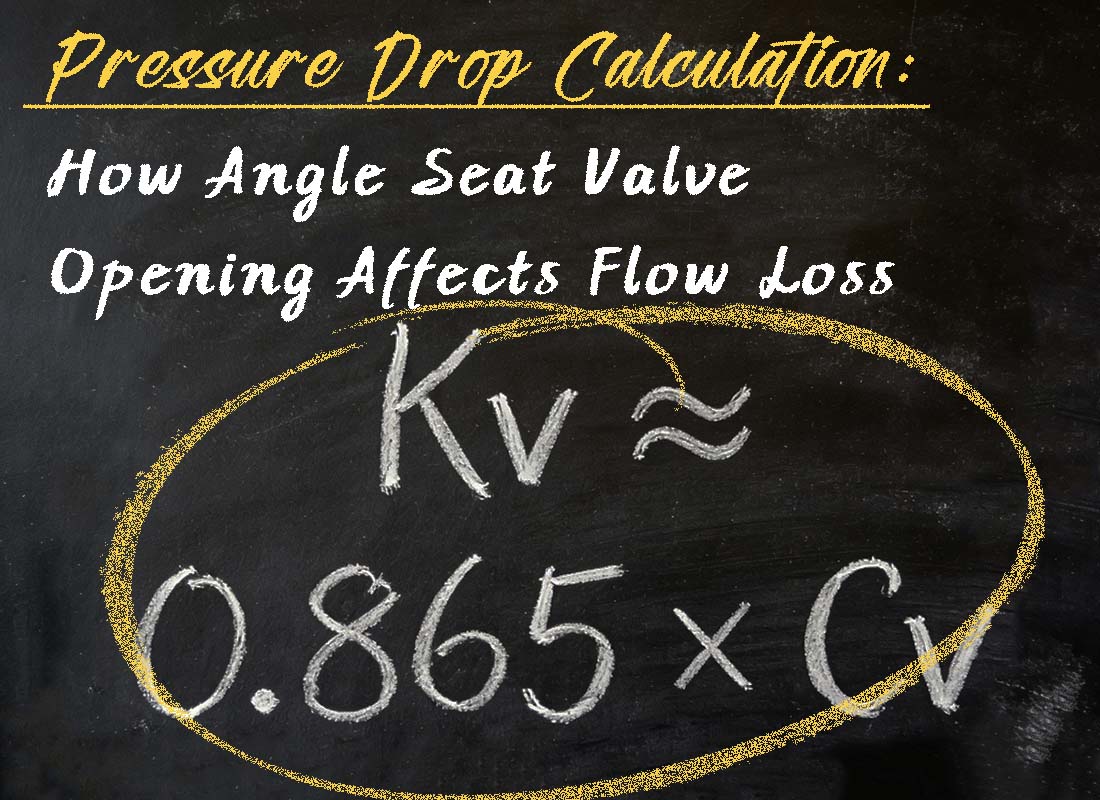 Pressure Drop Calculation: How Angle Seat Valve Opening Affects Flow Loss
Pressure Drop Calculation: How Angle Seat Valve Opening Affects Flow Loss
 IP Protection Rating of Solenoid Valve Coils
IP Protection Rating of Solenoid Valve Coils
You May Interest In



Dec 02, 2025 Blog
What are the parts of a pneumatic cylinder?












Apr 18, 2025 Blog
What is an Angle Seat Valve?Links: www.fescolo.com(Pneumatic)
FOKCA ©1998-2025 All Rights Reserved Sitemap