- sales@fokca.com info@fokca.com
- WhatsApp: +86 150 5749 1870
Aug 12, 2025
Solenoid valves are key components for fluid control in automation systems, mainly divided into two types: pilot-operated and direct-acting. This article will take you through a complete understanding of their working principles and structure.
A solenoid valve is a component that remotely regulates valve opening and closing by electromagnetic force to achieve automated fluid control.
· Power On: Applying current to the coil generates a magnetic field, which moves the plunger to open the valve.
· Power Off: When not energized, the valve stays in its default position—either open or closed.
· Fluid Flow: The valve maintains fluid flow by being fully open or blocks flow by being fully closed.
· Power Off Again: Cutting off current causes the sealing element to return to its default position.
In general, direct-acting solenoid valves are not suitable for regulating flow.
2-way: One inlet and one outlet; suitable for simple on/off control.
3-way: One inlet and two outlets; used to change fluid direction.
4-way: Two inlets and two outlets; used for more complex flow control.
General Solenoid Valves: Control fluid on/off, usually without flow regulation.
Pneumatic Solenoid Valves: Control pneumatic actuators, suitable for large diameter and high-pressure, high-thrust industries.
Pulse Solenoid Valves: Fast response with high-speed compressed air flow, commonly used in dust removal systems.
Enquire more solenoid valve types in our fokcaflow website.
These valves use a small pilot valve to control the main valve. When energized, the pilot valve opens, releasing medium into the main valve chamber, creating a pressure difference that moves the main valve spool to open the passage; when the pilot valve closes, the main valve closes accordingly.
Direct-acting valves operate without a pilot valve. The coil’s magnetic field directly drives the solenoid to open or close the valve spool.
Pressure: Pilot-operated valves can handle higher pressures.
Flow Rate: Pilot-operated valves are better suited for high flow applications.
Speed: Direct-acting valves respond faster.
Power Consumption: Direct-acting valves generally consume less power.
Both direct-acting and pilot-operated valves rely on electromagnetic force to drive the valve spool either directly or indirectly.
These valves are used in:
Agricultural Machinery: For irrigation systems and hydraulic control of farm equipment.
Oil and Gas: Controlling fluid flow in oil and gas extraction and transportation.
Food and Beverage Processing: Managing liquid raw materials and cleaning fluid transport.
Aerospace: Used in hydraulic and fuel management systems for flight control.
Paper Industry: Controlling slurry and additives flow to ensure stable production.
 How to Install Hydraulic Quick Hose Fittings and Couplers
How to Install Hydraulic Quick Hose Fittings and Couplers
 A Guide to Selecting Hydraulic Quick Fittings and Couplers
A Guide to Selecting Hydraulic Quick Fittings and Couplers
 Pneumatic manifold: the silent conductor of the automation system
Pneumatic manifold: the silent conductor of the automation system
 1/2 Inch Hydraulic Hose Couplers: Specifications, Installation, and Applications
1/2 Inch Hydraulic Hose Couplers: Specifications, Installation, and Applications
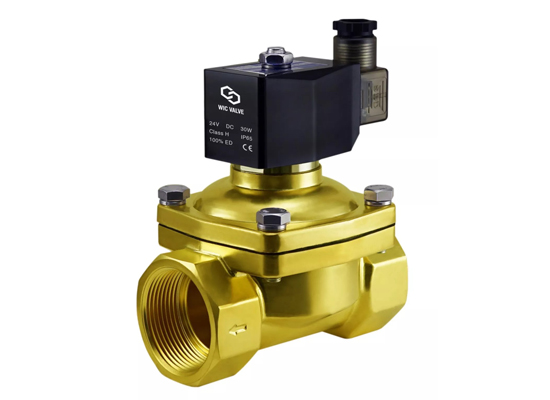 In-depth Analysis of Solenoid Valves: Principles, Structure, and Comprehensive Guide
In-depth Analysis of Solenoid Valves: Principles, Structure, and Comprehensive Guide
You May Interest In










Apr 18, 2025 Blog
What is an Angle Seat Valve?Links: www.fescolo.com(Pneumatic)
FOKCA ©1998-2025 All Rights Reserved Sitemap