Sep 22, 2025

Pneumatic products are widely used in industrial automation to generate, control, and transmit motion using compressed air. Compared with hydraulic or electric systems, pneumatics offer a cleaner structure, faster response, and simpler maintenance, which makes them especially suitable for manufacturing environments that require reliability, safety, and cost control.
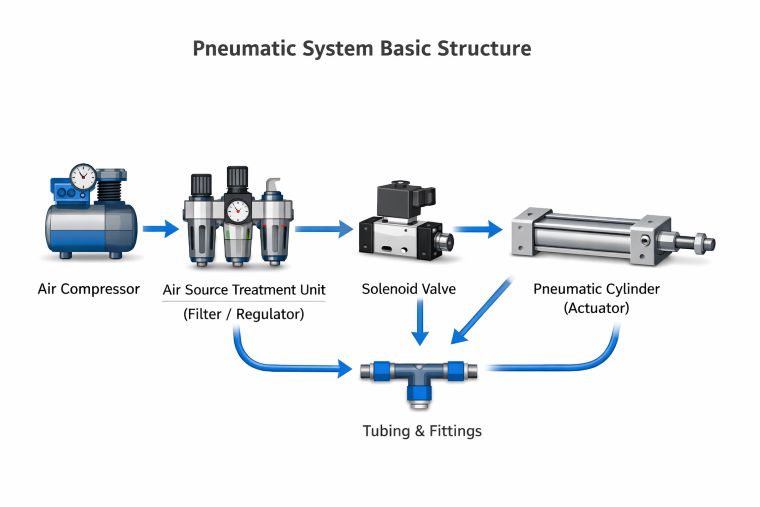
In practice, pneumatic products are not a single category but a complete system. This system usually includes Air Source Treatment Units, Pneumatic Solenoid Valves, and Air Cylinders, all working together to convert compressed air into stable mechanical movement. Understanding where and why these products are used helps engineers and buyers make more accurate selection decisions.

One of the most common applications of pneumatic products is automated production lines. Air Cylinders are used to perform linear movements such as pushing, lifting, clamping, positioning, and ejecting parts. In assembly lines, cylinders often handle repetitive tasks where speed and consistency matter more than precise force feedback.
Pneumatic Solenoid Valves play a critical role in these systems by controlling air flow direction, pressure, and timing. They are commonly integrated with PLC systems, allowing automated control of cylinders and actuators. This combination enables fast cycle times and stable operation, which is essential for high-volume manufacturing.
Because compressed air is easy to distribute across a factory, pneumatic systems scale well. Adding new stations or modifying existing processes usually requires minimal changes compared with hydraulic piping or electrical drives.
Pneumatic products are widely used in packaging machinery, especially in industries with strict hygiene requirements. Compressed air systems do not involve oil circulation in the working area, reducing the risk of contamination when properly designed.
In food and pharmaceutical equipment, pneumatic actuators are commonly used for:
· Opening and closing filling valves
· Positioning containers and trays
· Driving cutting, sealing, and labeling mechanisms
Air Source Treatment Units such as filters, regulators, and lubricators ensure that the compressed air quality meets equipment requirements. In sensitive applications, oil-free or low-lubrication pneumatic components are preferred to maintain clean operation.
Pneumatic products are also widely applied in material handling systems. Vacuum generators, Pneumatic Cylinders, and pneumatic grippers are used to pick, place, lift, and transfer items of various shapes and weights.
In logistics and warehousing, pneumatic components are often integrated into conveyor systems, sorting equipment, and palletizing machines. Air Hose and Tubings connect different components, allowing fast response and simple structure that enables reliable operation in continuous-duty environments.
Compared with electric actuators, pneumatic systems can tolerate dust, vibration, and temperature variations more effectively, making them suitable for harsh industrial conditions.
Many machine tools rely on pneumatic products for auxiliary functions. Air Cylinders are commonly used for tool clamping, workpiece positioning, and safety mechanisms. Pneumatic Solenoid Valves provide quick and repeatable control, ensuring consistent machine operation.
In CNC machines, compressed air is often used for chip removal, cooling assistance, and protective air curtains. These supporting functions may not directly drive motion, but they significantly improve machining efficiency and equipment lifespan.
In automotive production, pneumatic systems are used extensively in welding lines, assembly stations, and inspection equipment. Air Cylinders handle repetitive positioning tasks, while Pneumatic Solenoid Valves ensure stable holding during welding or fastening operations.
Electronics manufacturing also relies on pneumatic products, especially in pick-and-place equipment and testing devices. The lightweight nature of pneumatic actuators allows rapid movement without generating excessive heat, which is important when handling sensitive electronic components.
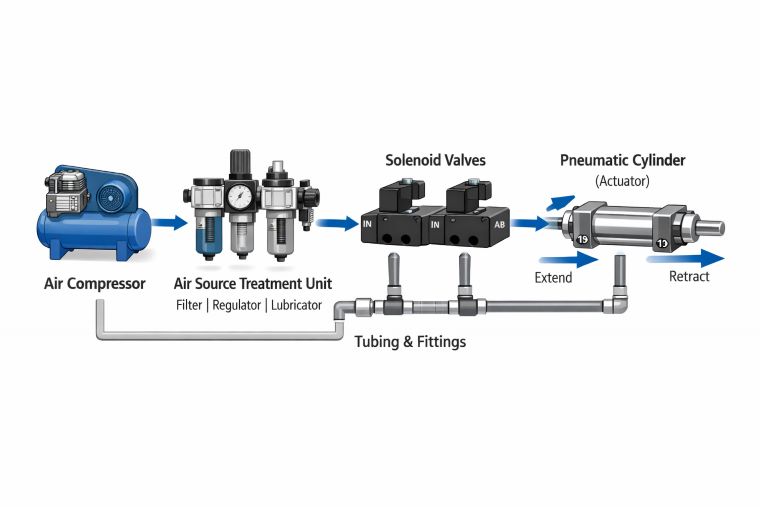
A complete pneumatic system usually includes several core product types:
· Air Source Treatment Units: filters, regulators, lubricators
· Pneumatic Solenoid Valves, mechanical valves, flow control valves
· Air Cylinders, rotary actuators, air motors
· Air Hose and Tubings, pneumatic fittings, quick couplings
· Pneumatic Muffler & Silencer
Each category plays a specific role, and system performance depends on correct matching rather than individual component quality alone.
When selecting pneumatic products, engineers typically focus on operating pressure, required force, cycle speed, installation space, and environmental conditions. Factors such as air quality, duty cycle, and maintenance accessibility also influence product choice.
From an application perspective, the most reliable pneumatic systems are those designed around real operating conditions rather than theoretical calculations alone. Proper sizing and component compatibility help avoid common issues such as unstable motion, excessive air consumption, or premature wear.
(FK9027)
 The principle and characteristics of vacuum generators
The principle and characteristics of vacuum generators
 Action Delay of 2-Way Solenoid Valve in Long-Pipe Installation
Action Delay of 2-Way Solenoid Valve in Long-Pipe Installation
 Pilot Orifice Blockage: Hidden Risk in Micro Passages of Solenoid Valve
Pilot Orifice Blockage: Hidden Risk in Micro Passages of Solenoid Valve
 Pneumatic Vacuum Filter: Design Differences between SMC Type and Common Filters
Pneumatic Vacuum Filter: Design Differences between SMC Type and Common Filters
 Why Your PU Tube Burst? The Truth About Temperature & Pressure
Why Your PU Tube Burst? The Truth About Temperature & Pressure
You May Interest In
Links: www.fescolo.com(Pneumatic)
FOKCA ©1998-2025 All Rights Reserved Sitemap