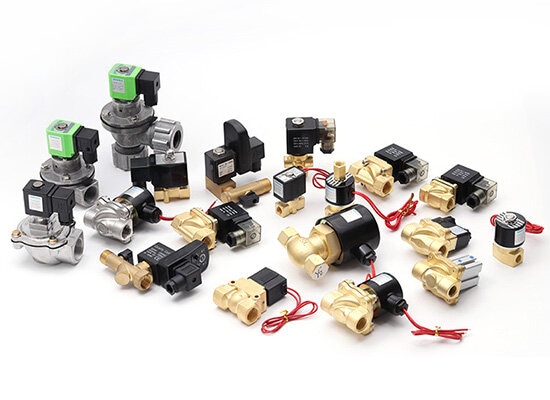
What Is a Solenoid Valve?Why it so Matter?
A solenoid valve is an automated control valve.The characteristic is that it relies on the electromagnetic force generated by the solenoid coil to drive the movement of the valve core and thus to open or regulate the fluids include gases or liquids. It converts electrical energy into mechanical motion, enabling remote, rapid, and high-frequency control. Solenoid valves are widely used in pneumatic, hydraulic, water treatment, HVAC, and industrial automation systems. They are essential components for automation due to their fast response, high efficiency, compact structure, small size, and compatibility with pneumatic actuators.

Working Principle of Solenoid valve
A solenoid valve is a basic automation control valve that uses electromagnetic force to control the switching and direction of fluid flow.A solenoid valve consists of a coil, a plunger, and a valve body. When an electric current passes through the coil, it generates a magnetic field that attracts the plunger, causing the valve to either open or close, depending on its design. When the current stops, a spring mechanism returns the plunger to its original position.
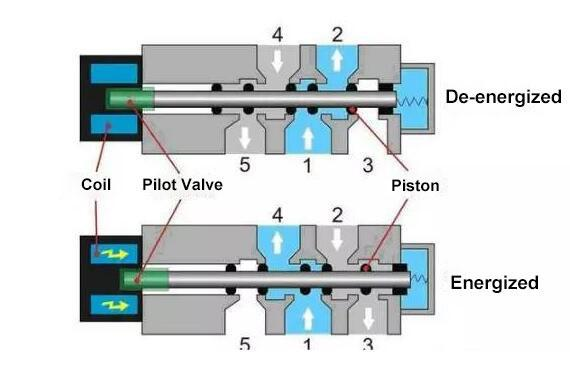
Types of Solenoid Valves
A solenoid valve is a basic automation control valve that uses electromagnetic force to control the switching and direction of fluid flow.According to their structure and driving method, they can be classified into various types.
◆ Direct-acting Solenoid Valves: These valves operate directly without the need for external pressure. They are typically used in low-flow applications.
◆ Pilot-operated Solenoid Valves: These valves use a small solenoid to control a larger diaphragm, allowing for the regulation of high-pressure fluids.
◆ Two-way Solenoid Valves: These valves have one inlet and one outlet and are used to either permit or block flow.
◆ Three-way Solenoid Valves: These have three ports and are used for diverting or mixing flows.
◆ Four-way Solenoid Valves: Typically found in pneumatic applications, these valves control the flow of air to actuators.
Applications of Solenoid Valve
A solenoid valve is a basic automation control valve that uses electromagnetic force to control the switching and direction of fluid flow.Mainly applied in the following fields:
◆ Industrial Automation: Used in manufacturing processes to control the flow of liquids and gases.
◆ Automotive Systems: Found in fuel injection systems, air conditioning, and transmission control.
◆ Medical Equipment: Used in devices such as oxygen delivery systems and dialysis machines.
◆ Household Appliances: Found in washing machines, dishwashers, and irrigation systems.
Advantages of solenoid valve
A solenoid valve is a basic automation control valve that uses electromagnetic force to control the switching and direction of fluid flow.It hsa multiple advantages.
◆ Fast Response Time: Solenoid valves operate almost instantaneously upon electrical activation.
◆ Energy Efficient: They consume power only when activated.
◆ Compact and Reliable: These valves have a small footprint and a long operational lifespan.
◆ Versatile: Suitable for various fluids, pressures, and temperature ranges.
If you want to learn more about solenoid or other types of valves, please visit our sub-site: https://www.fokcavalve.com/
FAQ
Q1.How to change solenoid valve?
To replace a solenoid valve, first disconnect the power supply and medium pressure. When removing the old valve, take note of the pipeline connections and wiring sequence. Before installing the new valve, verify the model and replace the sealing gaskets. Finally, reconnect the wiring and perform a functional test.
Q2.How to install solenoid valve?
The key to installing a solenoid valve lies in selecting the correct model and interface specifications based on the medium characteristics. Install it according to the flow direction arrow marked on the valve body, and after completing the wiring, power it on to test whether the opening and closing actions are normal.
Q3.How to fix solenoid valve?
Common steps for repairing a solenoid valve include cleaning internal impurities in the valve body, using a multimeter to check the continuity of the coil, and replacing worn components such as diaphragms or springs. After reassembly, it is essential to conduct tests for sealing performance and responsiveness. If the coil is burned out or the valve body is severely corroded, it is recommended to replace the valve entirely.

















