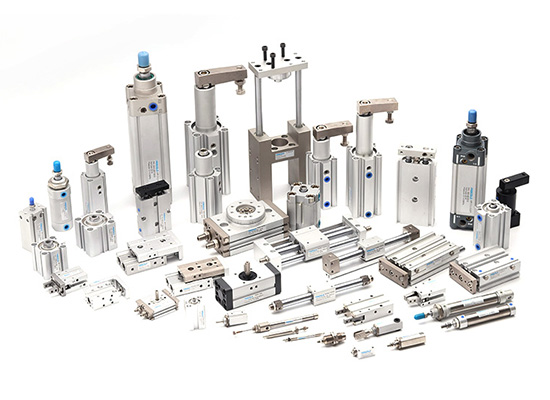
Pneumatic Components and System-Complete Guide
Pneumatic and Pneumatic system
Pneumatic components are independent yet interconnected devices powered by compressed air. When combined, they form a complete pneumatic system, which is widely used in automation, packaging, material handling, assembly lines, and industrial machinery.
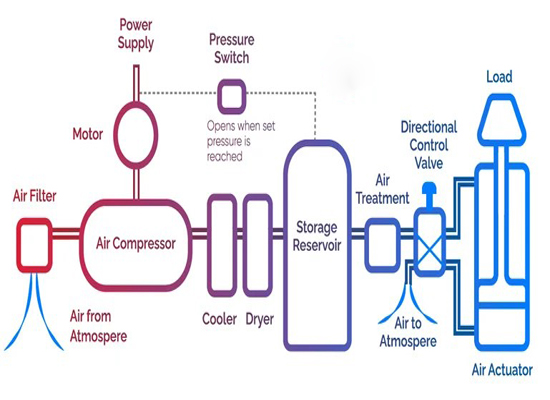
A modern pneumatic system consists of air preparation units, air storage, air transmission, control valves, and actuators. Because pneumatic technology is clean, fast, safe, and cost-effective, it has become one of the most widely used solutions in industrial automation.
What Are Pneumatic Components?
Pneumatic components have a simple and lightweight structure, fast response speed, easy maintenance, and low cost. They are widely used in industrial equipment, electrical automation systems, and electronics manufacturing.
Below are the five major categories of pneumatic components commonly found in industrial applications.
Types of pneumatic components
Pneumatic components consist of several different functional parts,But they can also play a connecting role in manufacturing industry with the transmission of compressed air.
◆ Preparation equipment:These Components that store, compress, and dry air include air receivers, compressors, dryers, and drain valves.
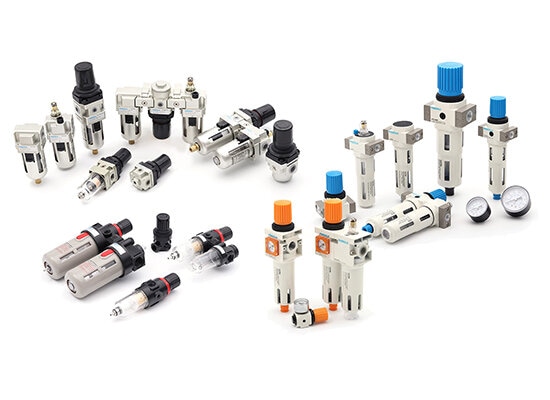
◆ Air source treatment units( FRL Units):A complete FRL (filter + regulator + lubricator) system provides clean, stable, and properly treated air for solenoid valves and cylinders. These unit may also include automatic drain valves and pressure gauges.
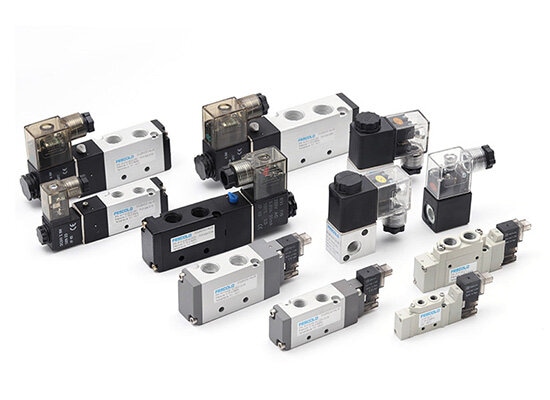
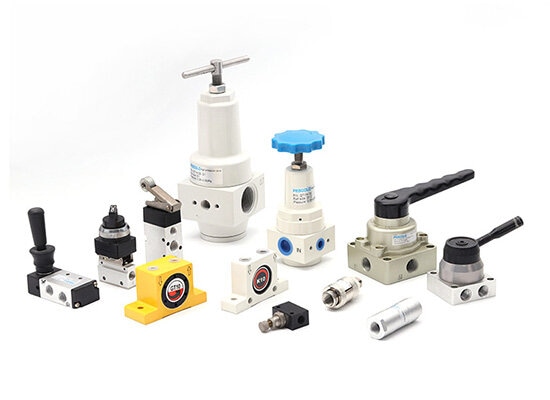
◆ Pneumatic Valves: Pneumatic valves control air direction, flow, and pressure.They are essential for coordinating the movement of cylinders and other actuators.They are usually divided into two primary types:
1.On/Off control valves – Simple open/close function.
2.Regulating valves – Adjust air flow and pressure.
◆ Pneumatic Hoses and Fittings: Pneumatic hoses and fittings deliver compressed air from valves to actuators. They must be leak-free, durable, bend-resistant, and sized to match the airflow.
◆ Pneumatic Actuators: These are the final action components that convert compressed air into mechanical motion such as pushing, pulling, lifting, rotating, or clamping. They come in various forms, including double-acting cylinders, single-acting cylinders, rotary actuators, and guided cylinders.
Advantages of Pneumatic Components In Industrial Automation
Pneumatic systems are widely preferred over hydraulic and electrical systems for several reasons:
Energy-Efficiency: One of the biggest advantages of using pneumatic components is that compressed air is easy to obtain and widely available.
Clean and Safe: Unlike hydraulic components,the pneumatic component has no oil leakage and is environmentally friendly.
Low Maintenance:Most Pneumatic elements have fewer moving parts and are less prone to wear and tear compared to other mechanical systems, reducing maintenance requirements.
Versatility: Pneumatic components can be used in a wide range of applications, from automation and packaging to robotics and material handling.
Modular and combinable:Various pneumatic components can be combined and used together, and the advantages of modular integration are very evident.
Pneumatic components application in automatical manufacturing
A pneumatic component is a fundamental element that forms the basis of pneumatic machines and automated equipment.
◆ Automatic assembly line
◆ Packaging Equipment
◆ Material Handling System
◆ Machine tool fixture system
◆ Welding and spraying equipment
◆ Testing and testing equipment
Pneumatic vs Hydraulic Components
Hydraulic Components:
Advantages
High torque and thrust: Hydraulic systems can generate significant force, making them suitable for heavy-load and high-pressure applications.
Precise control: Fast response enables accurate position control.
Disadvantages
Leakage risk: Hydraulic oil leaks can cause environmental pollution or equipment damage.
Complex maintenance: Hydraulic components are more complex and require higher maintenance effort.
High cost: Both initial investment and ongoing maintenance costs are generally higher.
Temperature sensitivity: The performance of hydraulic oil is greatly affected by temperature, limiting the working conditions of hydraulic systems.
Pneumatic Components:
Advantages
Simple and clean system: Uses compressed air or inert gases, which are clean and non-polluting.
Fast response: Pneumatic systems respond quickly, ideal for fast and frequent actions.
Easy maintenance: Due to simple structures, pneumatic systems are easier and cheaper to maintain.
Pneumatic components also have many limitation as follows:
Limited torque and thrust: Pneumatic systems produce less force and are not suitable for heavy-duty applications.
High air consumption: Compressed air requires significant energy to produce, resulting in lower efficiency.
Low control accuracy: The compressibility of air makes precise control more challenging.
By comparing with hydraulic components, you can see the advantages and focus of pneumatic components more clearly.
How to Maintain Pneumatic Components?
Pneumatic components, due to their simple structure and easy maintenance, require the following steps to be followed:
Cylinder Maintenance
Regularly check the lubricating oil and inspect the sealing components, replacing them promptly if necessary. Clean the surface of the cylinder, check the installation and connections to ensure the cylinder is securely fixed, and observe whether the cylinder operates smoothly without abnormal noises or sticking.
Valve Maintenance
Regularly clean the filter and valve core to remove impurities; inspect the solenoid valve coil to ensure there is no burning or broken wiring. Check the valve body’s sealing—poor sealing can cause air leakage. Manually or automatically test whether the valve opens and closes smoothly. Keep the exterior of the valve clean to prevent dust from entering the interior.
Tubing Maintenance
Regularly check that pipe connections are secure to prevent loosening and air leakage. Inspect the pipes for damage, aging, or cracks, and replace any damaged sections promptly. Avoid bending or crushing the pipes to maintain unobstructed airflow. Keep the pipes clean to prevent blockages and dust accumulation.
Fitting Maintenance
Ensure that fittings are tightly connected with no looseness or air leakage. Regularly inspect sealing rings or gaskets, and replace any aging components promptly. Avoid over-tightening to prevent damage to the fittings. Keep the fitting areas clean to prevent impurities from entering the airflow.
Moreover,there something you should do include:Monitor Pressure and Flow,Seal and Connection Integrity,Test Functional Performance,Documentation and Record Keeping.
What to Consider When Choosing a Supplier?
Finding professionals source pneumatic and hydraulic components suppliers is the key to ensure the components' performance, safety, energy-efficient and stability of pneumatic components and even pneumatic systems.Before making a purchase, you must consider the following:
Product Range & Specialization: Fully understand the supplier's product range and whether they have a specialized technical solution team.
Certifications: Do they have multiple certifications such as ISO, CE, RoHS, etc.
After-Sales Support: Does they have pre-sales and after-sales support.
Delivery & Lead Times: Ensure their logistics fit your production schedule.
Customer Reviews: Search for some relevant customer reviews and buyer solutions
For more details about our industruial pneumatic cylinders, please visit our dedicated pneumatic product Online.
FAQ
Q1: What are pneumatic components?
Pneumatic components are devices that use compressed air to perform mechanical actions, such as cylinders, valves, air compressors, and basic air treatment units.
Q2: What are the main components of a pneumatic system?
A pneumatic system is mainly composed of an air compressor, air treatment components, control components, actuators, and pneumatic tubes and fittings.
Q3:Can the various components of the pneumatic system be replaced?
The components of a pneumatic system are generally replaceable and and the material is pollution-free; however, replacement requires careful consideration of factors such as fitting compatibility, pressure ratings, functional equivalence, dimensions, and mounting requirements.
Q4.Are pneumatic components suitable for heavy-duty applications?
Yes,especially where fast, repetitive motion is required and precision is less critical. However, for tasks requiring very high force or pressure, hydraulic systems and hydraulics are often more suitable.